Wazuh Indexer Technical Documentation
This folder contains the technical documentation for the Wazuh Indexer. The documentation is organized into the following guides:
- Development Guide: Instructions for building, testing, and packaging the Indexer.
- Reference Manual: Detailed information on the Indexer’s architecture, configuration, and usage.
Requirements
To work with this documentation, you need mdBook installed.
-
Get the latest
cargo(hit enter when prompted for a default install)curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh -
Install
mdbookandmdbook-mermaidcargo install mdbook cargo install mdbook-mermaid
Usage
-
To build the documentation, run:
./build.shThe output will be generated in the
bookdirectory. -
To serve the documentation locally for preview, run:
./server.shThe documentation will be available at http://127.0.0.1:3000.
Development documentation
Under this section, you will find the development documentation of Wazuh Indexer. This documentation contains instructions to compile, run, test and package the source code. Moreover, you will find instructions to set up a development environment in order to get started at developing the Wazuh Indexer.
This documentation assumes basic knowledge of certain tools and technologies, such as Docker, Bash (Linux) or Git.
Set up the Development Environment
1. Git
Install and configure Git (SSH keys, commits and tags signing, user and email).
- Set your username.
- Set your email address.
- Generate an SSH key.
- Add the public key to your GitHub account for authentication and signing.
- Configure Git to sign commits with your SSH key.
2. Repositories
Clone the Wazuh Indexer repositories (use SSH). Before you start, you need to properly configure your working repositories to have origin and upstream remotes.
mkdir -p ~/wazuh && cd ~/wazuh
# Plugins (no upstream fork)
git clone git@github.com:wazuh/wazuh-indexer-plugins.git
# Indexer core (forked from OpenSearch)
git clone git@github.com:wazuh/wazuh-indexer.git
cd wazuh-indexer
git remote add upstream git@github.com:opensearch-project/opensearch.git
cd ..
# Reporting plugin (forked from OpenSearch)
git clone git@github.com:wazuh/wazuh-indexer-reporting.git
cd wazuh-indexer-reporting
git remote add upstream git@github.com:opensearch-project/reporting.git
cd ..
# Security Analytics (forked from OpenSearch)
git clone git@github.com:wazuh/wazuh-indexer-security-analytics.git
cd wazuh-indexer-security-analytics
git remote add upstream git@github.com:opensearch-project/security-analytics.git
cd ..
3. Vagrant
Install Vagrant with the Libvirt provider following the guide.
Then install the Vagrant SCP plugin:
vagrant plugin install vagrant-scp
4. IntelliJ IDEA
Prepare your IDE:
- Install IDEA Community Edition as per the official documentation.
- Set a global SDK to Eclipse Temurin following this guide.
You can find the JDK version to use under the
wazuh-indexer/gradle/libs.versions.tomlfile. IntelliJ IDEA includes some JDKs by default. If you need to change it, or if you want to use a different distribution, follow the instructions in the next section.
5. Set up Java
When you open a Java project for the first time, IntelliJ will ask you to install the appropriate JDK for the project.
Using IDEA, install a JDK following this guide. The version to install must match the JDK version used by the Indexer (check wazuh-indexer/gradle/libs.versions.toml).
Once the JDK is installed, configure it as the default system-wide Java installation using update-alternatives:
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java /home/$USER/.jdks/temurin-21.0.9/bin/java 0
Check Java is correctly configured:
java --version
If you need to install or switch JDK versions, use sudo update-alternatives --config java to select the JDK of your preference.
Set the JAVA_HOME and PATH environment variables by adding these lines to your shell RC file (.bashrc, .zshrc, etc.):
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/temurin-24-jdk-amd64
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/lib/jvm/temurin-24-jdk-amd64/bin
After that, restart your shell or run source ~/.zshrc (or similar) to apply the changes. Verify with java --version.
Tip: SDKMAN is a convenient tool for managing multiple JDK versions:
sdk install java 24-tem sdk use java 24-tem
6. Docker (Optional)
Docker is useful for running integration tests and local test environments. Install Docker Engine following the official instructions.
Verify the installation:
docker --version
docker run hello-world
7. Test Cluster (Optional)
The repository includes a Vagrant-based test cluster at tools/test-cluster/ for end-to-end testing against a real Wazuh Indexer instance.
Prerequisites:
- Vagrant
- VirtualBox or another supported provider
Refer to the tools/test-cluster/README.md for provisioning and usage instructions.
8. Verify the Setup
After completing the setup, verify everything works:
cd wazuh-indexer-plugins
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:compileJava
If compilation succeeds, your environment is ready. See Build from Sources for more build commands.
How to generate a package
This guide includes instructions to generate distribution packages locally using Docker.
Wazuh Indexer supports any of these combinations:
- distributions:
['tar', 'deb', 'rpm'] - architectures:
['x64', 'arm64']
Windows is currently not supported.
For more information navigate to the compatibility section.
Before you get started, make sure to clean your environment by running ./gradlew clean on the root level of the wazuh-indexer repository.
Pre-requisites
The process to build packages requires Docker and Docker Compose.
Your workstation must meet the minimum hardware requirements (the more resources the better ☺):
- 8 GB of RAM (minimum)
- 4 cores
The tools and source code to generate a package of Wazuh Indexer are hosted in the wazuh-indexer repository, so clone it if you haven’t done already.
Building wazuh-indexer packages
The Docker environment under wazuh-indexer/build-scripts/builder automates the build and assemble process for the Wazuh Indexer and its plugins, making it easy to create packages on any system.
Use the builder.sh script to build a package.
./builder.sh -h
Usage: ./builder.sh [args]
Arguments:
-p INDEXER_PLUGINS_BRANCH [Optional] wazuh-indexer-plugins repo branch, default is 'main'.
-r INDEXER_REPORTING_BRANCH [Optional] wazuh-indexer-reporting repo branch, default is 'main'.
-s SECURITY_ANALYTICS_BRANCH [Optional] wazuh-indexer-security-analytics repo branch, default is 'main'.
-R REVISION [Optional] Package revision, default is '0'.
-S STAGE [Optional] Staging build, default is 'false'.
-d DISTRIBUTION [Optional] Distribution, default is 'rpm'.
-a ARCHITECTURE [Optional] Architecture, default is 'x64'.
-D Destroy the docker environment
-h Print help
The example below it will generate a wazuh-indexer package for Debian based systems, for the x64 architecture, using 1 as revision number and using the production naming convention.
# Wihtin wazuh-indexer/build-scripts/builder
bash builder.sh -d deb -a x64 -R 1 -S true
The resulting package will be stored at wazuh-indexer/artifacts/dist.
The
STAGEoption defines the naming of the package. When set tofalse, the package will be unequivocally named with the commits’ SHA of thewazuh-indexer,wazuh-indexer-pluginsandwazuh-indexer-reportingrepositories, in that order. For example:wazuh-indexer_5.0.0-0_x86_64_aff30960363-846f143-494d125.rpm.
How to generate a container image
This guide includes instructions to generate distribution packages locally using Docker.
Wazuh Indexer supports any of these combinations:
- distributions:
['tar', 'deb', 'rpm'] - architectures:
['x64', 'arm64']
Windows is currently not supported.
For more information navigate to the compatibility section.
Before you get started, make sure to clean your environment by running ./gradlew clean on the root level of the wazuh-indexer repository.
Pre-requisites
The process to build packages requires Docker and Docker Compose.
Your workstation must meet the minimum hardware requirements (the more resources the better ☺):
- 8 GB of RAM (minimum)
- 4 cores
The tools and source code to generate a package of Wazuh Indexer are hosted in the wazuh-indexer repository, so clone it if you haven’t done already.
Building wazuh-indexer Docker images
The wazuh-indexer/build-scripts/docker folder contains the code to build Docker images. Below there is an example of the command needed to build the image. Set the build arguments and the image tag accordingly.
The Docker image is built from a wazuh-indexer tarball (tar.gz), which must be present in the same folder as the Dockerfile in wazuh-indexer/build-scripts/docker.
docker build \
--build-arg="VERSION=<version>" \
--build-arg="INDEXER_TAR_NAME=wazuh-indexer_<version>-<revision>_linux-x64.tar.gz" \
--tag=wazuh-indexer:<version>-<revision> \
--progress=plain \
--no-cache .
Then, start a container with:
docker run -p 9200:9200 -it --rm wazuh-indexer:<version>-<revision>
The build-and-push-docker-image.sh script automates the process to build and push Wazuh Indexer Docker images to our repository in quay.io. The script takes several parameters. Use the -h option to display them.
To push images, credentials must be set at environment level:
- QUAY_USERNAME
- QUAY_TOKEN
Usage: build-scripts/build-and-push-docker-image.sh [args]
Arguments:
-n NAME [required] Tarball name.
-r REVISION [Optional] Revision qualifier, default is 0.
-h help
The script will stop if the credentials are not set, or if any of the required parameters are not provided.
This script is used in the 5_builderpackage_docker.yml GitHub Workflow, which is used to automate the process even more. When possible, prefer this method.
How to Build from Sources
The Wazuh Indexer Plugins repository uses Gradle as its build system. The root project contains multiple subprojects, one per plugin.
Building the Entire Project
To build all plugins (compile, test, and package):
./gradlew build
When completed, distribution artifacts for each plugin are located in their respective build/distributions/ directories.
Building a Specific Plugin
To build only the Content Manager plugin:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:build
Other plugin targets follow the same pattern. To see all available projects:
./gradlew projects
Compile Only (No Tests)
For a faster feedback loop during development, compile without running tests:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:compileJava
This is useful for checking that your code changes compile correctly before running the full test suite.
Output Locations
| Artifact | Location |
|---|---|
| Plugin ZIP distribution | plugins/<plugin-name>/build/distributions/ |
| Compiled classes | plugins/<plugin-name>/build/classes/ |
| Test reports | plugins/<plugin-name>/build/reports/tests/ |
| Generated JARs | plugins/<plugin-name>/build/libs/ |
Common Build Issues
JDK Version Mismatch
The project requires a specific JDK version (currently JDK 24, Eclipse Temurin). If you see compilation errors related to Java version, check:
java --version
Ensure JAVA_HOME points to the correct JDK. See Setup for details.
Dependency Resolution Failures
If Gradle cannot resolve dependencies:
- Check your network connection (dependencies are downloaded from Maven Central and repositories).
- Try clearing the Gradle cache:
rm -rf ~/.gradle/caches/ - Re-run with
--refresh-dependencies:./gradlew build --refresh-dependencies
Out of Memory
For large builds, increase Gradle’s heap size in gradle.properties:
org.gradle.jvmargs=-Xmx4g
Linting and Formatting Errors
The build includes code quality checks (Spotless, etc.). If formatting checks fail:
./gradlew spotlessApply
Then rebuild.
Useful Gradle Flags
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
--info | Verbose output |
--debug | Debug-level output |
--stacktrace | Print stack traces on failure |
--parallel | Run tasks in parallel (faster on multi-core) |
-x test | Skip tests: ./gradlew build -x test |
--continuous | Watch mode — rebuilds on file changes |
How to run from sources
Every Wazuh Indexer repository includes one or more Gradle projects with predefined tasks to run and build the source code.
In this case, to run a Gradle project from source code, run the ./gradlew run command.
For Wazuh Indexer, additional plugins may be installed by passing the -PinstalledPlugins flag:
./gradlew run -PinstalledPlugins="['plugin1', 'plugin2']"
The ./gradlew run command will build and start the project, writing its log above Gradle’s status message. A lot of stuff is logged on startup, specifically these lines tell you that OpenSearch is ready.
[2020-05-29T14:50:35,167][INFO ][o.e.h.AbstractHttpServerTransport] [runTask-0] publish_address {127.0.0.1:9200}, bound_addresses {[::1]:9200}, {127.0.0.1:9200}
[2020-05-29T14:50:35,169][INFO ][o.e.n.Node ] [runTask-0] started
It’s typically easier to wait until the console stops scrolling, and then run curl in another window to check if OpenSearch instance is running.
curl localhost:9200
{
"name" : "runTask-0",
"cluster_name" : "runTask",
"cluster_uuid" : "oX_S6cxGSgOr_mNnUxO6yQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "1.0.0-SNAPSHOT",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "0ba0e7cc26060f964fcbf6ee45bae53b3a9941d0",
"build_date" : "2021-04-16T19:45:44.248303Z",
"build_snapshot" : true,
"lucene_version" : "8.7.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
}
}
Use -Dtests.opensearch. to pass additional settings to the running instance. For example, to enable OpenSearch to listen on an external IP address, pass -Dtests.opensearch.http.host. Make sure your firewall or security policy allows external connections for this to work.
./gradlew run -Dtests.opensearch.http.host=0.0.0.0
How to Run the Tests
This section explains how to run the Wazuh Indexer Plugins tests at various levels.
Full Suite
To execute all tests and code quality checks (linting, documentation, formatting):
./gradlew check
This runs unit tests, integration tests, and static analysis tasks.
Unit Tests
Run all unit tests across the entire project:
./gradlew test
Run unit tests for a specific plugin:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:test
Integration Tests
Run integration tests for a specific plugin:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:integTest
YAML REST Tests
Plugins can define REST API tests using YAML test specs. To run them:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:yamlRestTest
Reproducible Test Runs
Tests use randomized seeds. When a test fails, the output includes the seed that was used. To reproduce the exact same run:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:test -Dtests.seed=DEADBEEF
Replace DEADBEEF with the actual seed from the failure output.
Viewing Test Reports
After running tests, HTML reports are generated at:
plugins/<plugin-name>/build/reports/tests/test/index.html
Open this file in a browser to see detailed results with pass/fail status, stack traces, and timing.
For integration tests:
plugins/<plugin-name>/build/reports/tests/integTest/index.html
Running a Single Test Class
To run a specific test class:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:test --tests "com.wazuh.contentmanager.rest.service.RestPostRuleActionTests"
Test Cluster (Vagrant)
For end-to-end testing on a real Wazuh Indexer service, the repository includes a Vagrant-based test cluster at tools/test-cluster/. This provisions a virtual machine with Wazuh Indexer installed and configured.
Refer to its README.md for setup and usage instructions.
Package Testing
Smoke tests on built packages are run via GitHub Actions Workflows. These install packages on supported operating systems:
- DEB packages — installed on the Ubuntu 24.04 GitHub Actions runner.
- RPM packages — installed in a Red Hat 9 Docker container.
Useful Test Flags
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
-Dtests.seed=<seed> | Reproduce a specific randomized test run |
-Dtests.verbose=true | Print test output to stdout |
--tests "ClassName" | Run a single test class |
--tests "ClassName.methodName" | Run a single test method |
-x test | Skip unit tests in a build |
Wazuh Indexer Setup Plugin — Development Guide
This document describes how to extend the Wazuh Indexer setup plugin to create new index templates and index management policies (ISM) for OpenSearch.
📦 Creating a New Index
1. Add a New Index Template
Create a new JSON file in the directory: /plugins/setup/src/main/resources
Follow the existing structure and naming convention. Example:
{
"index_patterns": ["<pattern>"],
"mappings": {
"date_detection": false,
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
<custom mappings and fields>
}
},
"order": 1,
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}
}
2. Register the Index in the Code
Edit the constructor of the SetupPlugin class located at: /plugins/setup/src/main/java/com/wazuh/setup/SetupPlugin.java
Add the template and index entry to the indices map. There are two kind of indices:
- Stream index. Stream indices contain time-based events of any kind (alerts, statistics, logs…).
- Stateful index. Stateful indices represent the most recent information of a subject (active vulnerabilities, installed packages, open ports, …). These indices are different of Stream indices as they do not contain timestamps. The information is not based on time, as they always represent the most recent state.
/**
* Main class of the Indexer Setup plugin. This plugin is responsible for the creation of the index
* templates and indices required by Wazuh to work properly.
*/
public class SetupPlugin extends Plugin implements ClusterPlugin {
// ...
// Stream indices
this.indices.add(new StreamIndex("my-stream-index-000001", "my-index-template-1", "my-alias"));
// State indices
this.indices.add(new StateIndex("my-state-index", "my-index-template-2"));
//...
}
✅ Verifying Template and Index Creation After building the plugin and deploying the Wazuh Indexer with it, you can verify the index templates and indices using the following commands:
curl -X GET <indexer-IP>:9200/_index_template/ curl -X GET <indexer-IP>:9200/_cat/indices?v
Alternatively, use the Developer Tools console from the Wazuh Dashboard, or your browser.
🔁 Creating a New ISM (Index State Management) Policy
1. Add Rollover Alias to the Index Template
Edit the existing index template JSON file and add the following setting:
"plugins.index_state_management.rollover_alias": "<index-name>"
2. Define the ISM Policy
Refer to the OpenSearch ISM Policies documentation for more details.
Here is an example ISM policy:
{
"policy": {
"policy_id": "<index-name>-rollover-policy",
"description": "<policy-description>",
"last_updated_time": <unix-timestamp-in-milliseconds>,
"schema_version": 21,
"error_notification": null,
"default_state": "rollover",
"states": [
{
"name": "rollover",
"actions": [
{
"rollover": {
"min_doc_count": 200000000,
"min_index_age": "7d",
"min_primary_shard_size": "25gb"
}
}
],
"transitions": []
}
],
"ism_template": [
{
"index_patterns": [
"wazuh-<pattern1>-*"
// Optional additional patterns
// "wazuh-<pattern2>-*"
],
"priority": <priority-int>,
"last_updated_time": <unix-timestamp-in-milliseconds>
}
]
}
}
3. Register the ISM Policy in the Plugin Code
Edit the IndexStateManagement class located at: /plugins/setup/src/main/java/com/wazuh/setup/index/IndexStateManagement.java
Register the new policy constant and add it in the constructor:
// ISM policy name constant (filename without .json extension)
static final String MY_POLICY = "my-policy-filename";
...
/**
* Constructor
*
* @param index Index name
* @param template Index template name
*/
public IndexStateManagement(String index, String template) {
super(index, template);
this.policies = new ArrayList<>();
// Register the ISM policy to be created
this.policies.add(MY_POLICY);
}
📌 Additional Notes
Always follow existing naming conventions to maintain consistency.
Use epoch timestamps (in milliseconds) for last_updated_time fields.
ISM policies and templates must be properly deployed before the indices are created.
🚀 Unclassified Events Data Stream (wazuh-events-v5-unclassified)
Overview
The wazuh-events-v5-unclassified data stream is a specialized stream designed to capture and store events that do not match any predefined event categories. This provides visibility into edge cases, parsing failures, and events that may require new categorization rules.
Purpose
- Investigation and Troubleshooting: Analyze uncategorized events to identify patterns or issues
- Rule Development: Identify events that need new categorization rules
- System Monitoring: Track parsing failures and anomalies
Data Stream Configuration
Index Template
- Location:
plugins/setup/src/main/resources/templates/streams/unclassified.json - Index Pattern:
wazuh-events-v5-unclassified* - Rollover Alias:
wazuh-events-v5-unclassified - Priority: 1 (higher priority than standard event streams for proper template selection)
Fields Included
- @timestamp: Event timestamp
- event.original: Raw, unprocessed event data
- wazuh.agent.*: Agent metadata (id, name, version, type)
- wazuh.cluster.*: Cluster information (name, node)
- wazuh.space.name: Wazuh space/tenant information
- wazuh.schema.version: Schema version
- wazuh.integration.*: Integration metadata (category, name, decoders, rules)
Storage Settings
- Number of Shards: 3
- Number of Replicas: 0
- Auto-expand Replicas: 0-1
- Refresh Interval: 5 seconds
- Dynamic Mapping: Strict (prevents unintended field creation)
ISM Policy
Policy Details
- Policy Name:
stream-unclassified-events-policy - Location:
plugins/setup/src/main/resources/policies/stream-unclassified-events-policy.json - Retention Period: 7 days
- Priority: 100
Policy States
-
Hot State
- Actions: None (events are immediately indexed)
- Transition Condition: Transitions to
deleteafter 7 days
-
Delete State
- Actions: Deletes the index
- Retry Policy: 3 attempts with exponential backoff (1-minute initial delay)
Use Cases
-
Event Classification Issues
- Events that failed to match any category
- Malformed or unusual event formats
-
Parsing Failures
- Events that couldn’t be decoded properly
- Invalid event structures
-
Rule Development
- Analyzing patterns that require new rules
- Edge cases not covered by existing rules
-
System Diagnostics
- Understanding integration performance
- Identifying missing integrations or decoders
Configuration
The data stream is created automatically during plugin initialization. Ensure:
- The template file
unclassified.jsonexists intemplates/streams/ - The ISM policy file
stream-unclassified-events-policy.jsonexists inpolicies/ - Both are registered in
SetupPlugin.javaandIndexStateManagement.java
Indexing Unclassified Events
To index events into this data stream, use:
POST /wazuh-events-v5-unclassified/_doc
{
"@timestamp": "2024-02-19T10:00:00Z",
"event": {
"original": "raw uncategorized event data"
},
"wazuh": {
"agent": {
"id": "001",
"name": "agent-name"
},
"space": {
"name": "default"
}
}
}
Monitoring and Analysis
Query Unclassified Events
GET /wazuh-events-v5-unclassified/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
Count Events by Agent
GET /wazuh-events-v5-unclassified/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"events_by_agent": {
"terms": {
"field": "wazuh.agent.id",
"size": 100
}
}
}
}
Time-based Analysis
GET /wazuh-events-v5-unclassified/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"events_over_time": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"interval": "1h"
}
}
}
}
Testing
Integration tests for the unclassified data stream are located at:
plugins/setup/src/test/java/com/wazuh/setup/UnclassifiedEventsIT.java
These tests verify:
- Data stream creation
- Template application
- ISM policy creation and application
- Document indexing capability
- Correct field mappings
Defining default users and roles for Wazuh Indexer
The Wazuh Indexer packages include a set of default users and roles specially crafted for Wazuh’s use cases. This guide provides instructions to extend or modify these users and roles so they end up being included in the Wazuh Indexer package by default.
Note that the access control and permissions management are handled by the OpenSearch’s security plugin. As a result, we provide configuration files for it. The data is applied during the cluster’s initialization, as a result of running the indexer-security-init.sh script.
Considerations and conventions
As these configuration files are included in the Wazuh Indexer package, they are hosted in the wazuh-indexer repository. Be aware of that when reading this guide.
Any security related resource (roles, action groups, users, …) created by us must be reserved (reserved: true). This ensures they cannot be modified by the users, in order to guarantee the correct operation of Wazuh Central Components. Also, they should be visible (hidden: false) unless explicitly defined otherwise.
1. Adding a new user
Add the new user to the internal_users.wazuh.yml file located at: wazuh-indexer/distribution/src/config/security/.
new-user:
# Generate the hash using the tool at `plugins/opensearch-security/tools/hash.sh -p <new-password>`
hash: "<HASHED-PASSWORD>"
reserved: true
hidden: false
backend_roles: []
description: "New user description"
OpenSearch’s reference:
2. Adding a new role
Add the new role to the roles.wazuh.yml file located at: wazuh-indexer/distribution/src/config/security/.
- Under
index_permissions.index_patterns, list the index patterns the role will have effect on. - Under
index_permissions.allowed_actions, list the allowed action groups or indiviual permissions granted to this role.
The default action groups for cluster_permissions and index_permissions are listed in the Default action groups documentation
role-read:
reserved: true
hidden: false
cluster_permissions: []
index_permissions:
- index_patterns:
- "wazuh-*"
dls: ""
fls: []
masked_fields: []
allowed_actions:
- "read"
tenant_permissions: []
static: true
role-write:
reserved: true
hidden: false
cluster_permissions: []
index_permissions:
- index_patterns:
- "wazuh-*"
dls: ""
fls: []
masked_fields: []
allowed_actions:
- "index"
tenant_permissions: []
static: true
OpenSearch’s reference:
3. Adding a new role mapping
Add the new role mapping to roles_mapping.wazuh.yml file located at: wazuh-indexer/distribution/src/config/security/. Note that the mapping name must match the role name.
- Under
users, list the users the role will be mapped to.
role-read:
reserved: true
hidden: false
backend_roles: [ ]
hosts: [ ]
users:
- "new-user"
and_backend_roles: [ ]
role-write:
reserved: true
hidden: false
backend_roles: [ ]
hosts: [ ]
users:
- "new-user"
and_backend_roles: [ ]
OpenSearch’s reference:
Testing the configuration
The validation of the new configuration needs to be tested on a running deployment of Wazuh Indexer containing the security plugin.
You can follow any of these paths:
A. Generating a new Wazuh Indexer package
- Apply your changes to the configuration files in
wazuh-indexer/distribution/src/config/security/. - Generate a new package (see Build Packages).
- Follow the official installation and configuration steps.
- Check the new changes are applied (you can use the UI or the API).
B. Applying the new configuration to an existing Wazuh Indexer deployment (using the UI or API)
- Use the Wazuh Indexer API or the Wazuh Dashboard to create a new security resource. Follow the steps in Defining users and roles.
C. Applying the new configuration to an existing Wazuh Indexer deployment (using configuration files)
- Add the new configuration to the affected file within
/etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-security/. - Run the
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/indexer-security-init.shscript to load the new configuration.
The indexer-security-init.sh will overwrite your security configuration, including passwords. Use it under your own risk.
Alternatively, apply the new configuration using fine-grained options. See Applying changes to configuration files
Wazuh Indexer Reporting Plugin — Development Guide
This document describes how to build a Wazuh Reporting plugin development environment to create and test new features.
Working from a minimal environment
In order to deploy a minimal environment for developing the reporting plugin just for testing purposes, you must have at least a Wazuh Indexer and a Wazuh Dashboard environment running. Then, you can create your own SMPT server to test the email notifications from the following Mailpit configuration. To verify everything is working correctly, try generating reports following the user’s guide.
Working from real scenario packages
Preparing packages
- Wazuh Indexer package (debian package based on OpenSearch 3.1.0). Compiled locally using the Docker builder:
bash builder.sh -d deb -a x64. - Wazuh Dashboard package (debian package based on OpenSearch 3.1.0). Downloaded from wazuh-dashboard actions.
Note: To test using RPM packages, update the Vagrant configuration and provisioning scripts accordingly (for example, change
generic/ubuntu2204togeneric/centos7in the Vagrantfile and replace Debian-specific installation commands with RPM equivalents).
Preparing a development environment
Prepare a multi-VM Vagrant environment with the following components:
- Server
- Wazuh Indexer (including the reporting plugin).
- Wazuh Dashboard (including the reporting plugin).
- Mailpit
- Mailpit SMTP server.
File location should be:
working-dir/
├── Vagrantfile
├── data/
│ ├── wazuh-indexer_*.deb
│ ├── wazuh-dashboard_*.deb
│ ├── gencerts.sh
│ ├── mailpit.sh
│ └── server.sh
Vagrantfile
Details
class VagrantPlugins::ProviderVirtualBox::Action::Network
def dhcp_server_matches_config?(dhcp_server, config)
true
end
end
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define "server" do |server|
server.vm.box = "generic/ubuntu2204"
server.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "8192"
end
# For Hyper-V provider
#server.vm.provider "hyperv" do |hv|
# hv.memory = 8192
#end
server.vm.network "private_network", type: "dhcp"
server.vm.hostname = "rhel-server"
config.vm.provision "file", source: "data", destination: "/tmp/vagrant_data"
server.vm.provision "shell", privileged: true, path: "data/server.sh"
end
config.vm.define "mailpit" do |mailpit|
mailpit.vm.box = "generic/ubuntu2204"
mailpit.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "1024"
end
# For Hyper-V provider
#client.vm.provider "hyperv" do |hv|
# hv.memory = 8192
#end
mailpit.vm.network "private_network", type: "dhcp"
mailpit.vm.hostname = "mailpit"
config.vm.provision "file", source: "data", destination: "/tmp/vagrant_data"
mailpit.vm.provision "shell", privileged: true, path: "data/mailpit.sh"
end
end
server.sh
Details
#!/bin/bash
# Install
dpkg -i /tmp/vagrant_data/wazuh-indexer*.deb
dpkg -i /tmp/vagrant_data/wazuh-dashboard*.deb
# Setup
## Create certs
mkdir certs
cd certs || exit 1
bash /tmp/vagrant_data/gencerts.sh .
mkdir -p /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs
cp admin.pem /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/admin.pem
cp admin.key /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/admin-key.pem
cp indexer.pem /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/indexer.pem
cp indexer-key.pem /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/indexer-key.pem
cp ca.pem /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/root-ca.pem
chown -R wazuh-indexer.wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/
mkdir -p /etc/wazuh-dashboard/certs
cp dashboard.pem /etc/wazuh-dashboard/certs/dashboard.pem
cp dashboard-key.pem /etc/wazuh-dashboard/certs/dashboard-key.pem
cp ca.pem /etc/wazuh-dashboard/certs/root-ca.pem
chown -R wazuh-dashboard.wazuh-dashboard /etc/wazuh-dashboard/certs/
systemctl daemon-reload
## set up Indexer
systemctl enable wazuh-indexer
systemctl start wazuh-indexer
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/indexer-security-init.sh
## set up Dashboard
systemctl enable wazuh-dashboard
systemctl start wazuh-dashboard
## enable IPv6
modprobe ipv6
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0
## turn off firewalld
sudo ufw disable
mailpit.sh
Details
#!/bin/bash
# Install
curl -sOL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/axllent/mailpit/develop/install.sh && INSTALL_PATH=/usr/bin sudo bash ./install.sh
# Setup
## set up Mailpit
useradd -r -s /bin/false mailpit
groupadd -r mailpit
### Create directories
mkdir -p /var/lib/mailpit
chown -R mailpit.mailpit /var/lib/mailpit
### Create password file
mkdir -p /etc/mailpit
echo "admin:$(openssl passwd -apr1 admin)" > /etc/mailpit/passwords
chown -R mailpit.mailpit /var/lib/mailpit
## Create certs
mkdir certs
cd certs || exit 1
bash /tmp/vagrant_data/gencerts.sh .
mkdir -p /etc/mailpit/certs
cp admin.pem /etc/mailpit/certs/admin.pem
cp admin.key /etc/mailpit/certs/admin-key.pem
cp mailpit.pem /etc/mailpit/certs/mailpit.pem
cp mailpit-key.pem /etc/mailpit/certs/mailpit-key.pem
cp ca.pem /etc/mailpit/certs/root-ca.pem
chown -R mailpit.mailpit /etc/mailpit/certs/
## enable IPv6
modprobe ipv6
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0
## turn off firewalld
sudo ufw disable
echo "======================================================"
echo "Start Mailpit with the following command:"
echo ""
echo "mailpit --listen 0.0.0.0:8025 --smtp 0.0.0.0:1025 --database /var/lib/mailpit.db --ui-auth-file /etc/mailpit/passwords --ui-tls-cert /etc/mailpit/certs/admin.pem --ui-tls-key /etc/mailpit/certs/admin-key.pem --smtp-tls-cert /etc/mailpit/certs/mailpit.pem --smtp-tls-key /etc/mailpit/certs/mailpit-key.pem"
echo "======================================================"
# Adding HTTPS: https://mailpit.axllent.org/docs/configuration/http/
# mailpit --ui-tls-cert /path/to/cert.pem --ui-tls-key /path/to/key.pem
# Adding basic authentication: https://mailpit.axllent.org/docs/configuration/passwords/
# mailpit --ui-auth-file /path/to/password-file
gencerts.sh
Details
#!/bin/bash
if [[ $# -ne 1 ]]; then
fs=$(mktemp -d)
else
fs=$1
shift
fi
echo Working directory $fs
cd $fs
if [[ ! -e $fs/cfssl ]]; then
curl -s -L -o $fs/cfssl https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssl_linux-amd64
curl -s -L -o $fs/cfssljson https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssljson_linux-amd64
chmod 755 $fs/cfssl*
fi
cfssl=$fs/cfssl
cfssljson=$fs/cfssljson
if [[ ! -e $fs/ca.pem ]]; then
cat << EOF | $cfssl gencert -initca - | $cfssljson -bare ca -
{
"CN": "Wazuh",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "US",
"L": "San Francisco",
"O": "Wazuh",
"OU": "Wazuh Root CA"
}
]
}
EOF
fi
if [[ ! -e $fs/ca-config.json ]]; then
$cfssl print-defaults config > ca-config.json
fi
gencert_rsa() {
name=$1
profile=$2
cat << EOF | $cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem -ca-key=ca-key.pem -config=ca-config.json -profile=$profile -hostname="$name,127.0.0.1,localhost" - | $cfssljson -bare $name -
{
"CN": "$i",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "US",
"L": "California",
"O": "Wazuh",
"OU": "Wazuh"
}
],
"hosts": [
"$i",
"localhost"
]
}
EOF
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -inform pem -in $name-key.pem -outform pem -nocrypt -out $name.key
}
gencert_ec() {
openssl ecparam -name secp256k1 -genkey -noout -out jwt-private.pem
openssl ec -in jwt-private.pem -pubout -out jwt-public.pem
}
hosts=(indexer dashboard mailpit)
for i in "${hosts[@]}"; do
gencert_rsa $i www
done
users=(admin)
for i in "${users[@]}"; do
gencert_rsa $i client
done
gencert_ec
- Bring up the environment with
vagrant up. Use the command provided in the console to start mailpit from within its VM. mailpit is configured to use TLS and access credentials (admin:admin). Useip addrto check for the public IP address given to the VM and use that IP to access mailpit UI (e.g:https://172.28.128.136:8025/). - Add the username and password for mailpit to the Wazuh Indexer keystore.
echo "admin" | /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/opensearch-keystore add opensearch.notifications.core.email.mailpit.username echo "admin" | /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/opensearch-keystore add opensearch.notifications.core.email.mailpit.password chown wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.keystore - Ensure
mailpitis accessible within theserverVM (e.gcurl https://172.28.128.136:8025 -k -u admin:adminshould return HTML code). If not, add it to the list of known hosts in/etc/hosts(e.gecho "172.28.128.136 mailpit mailpit" >> /etc/hosts).
Wazuh Indexer Content Manager Plugin — Development Guide
This document describes the architecture, components, and extension points of the Content Manager plugin, which manages security content synchronization from the Wazuh CTI API and provides REST endpoints for user-generated content management.
Overview
The Content Manager plugin handles:
- CTI Subscription: Manages subscriptions and tokens with the CTI Console.
- Job Scheduling: Periodically checks for updates using the OpenSearch Job Scheduler.
- Content Synchronization: Keeps local indices in sync with the Wazuh CTI Catalog via snapshots and incremental JSON Patch updates.
- Security Analytics Integration: Pushes rules, integrations, and detectors to the Security Analytics Plugin (SAP).
- User-Generated Content: Full CUD for rules, decoders, integrations, KVDBs, and policies in the Draft space.
- Engine Communication: Validates and promotes content via Unix Domain Socket to the Wazuh Engine.
- Space Management: Manages content lifecycle through Draft → Test → Custom promotion.
System Indices
The plugin manages the following indices:
| Index | Purpose |
|---|---|
.cti-consumers | Sync state (offsets, snapshot links) |
.cti-policies | Policy documents |
.cti-integrations | Integration definitions |
.cti-rules | Detection rules |
.cti-decoders | Decoder definitions |
.cti-kvdbs | Key-value databases |
.cti-iocs | Indicators of Compromise |
.engine-filters | Engine filter rules |
.wazuh-content-manager-jobs | Job scheduler metadata |
Plugin Architecture
Entry Point
ContentManagerPlugin is the main class. It implements Plugin, ClusterPlugin, JobSchedulerExtension, and ActionPlugin. On startup it:
- Initializes
PluginSettings,ConsumersIndex,CtiConsole,CatalogSyncJob,EngineServiceImpl, andSpaceService. - Registers all REST handlers via
getRestHandlers(). - Creates the
.cti-consumersindex on cluster manager nodes. - Schedules the periodic
CatalogSyncJobvia the OpenSearch Job Scheduler. - Optionally triggers an immediate sync on start.
REST Handlers
The plugin registers 22 REST handlers, grouped by domain:
| Domain | Handler | Method | URI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subscription | RestGetSubscriptionAction | GET | /_plugins/_content_manager/subscription |
RestPostSubscriptionAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/subscription | |
RestDeleteSubscriptionAction | DELETE | /_plugins/_content_manager/subscription | |
| Update | RestPostUpdateAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/update |
| Logtest | RestPostLogtestAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/logtest |
| Policy | RestPutPolicyAction | PUT | /_plugins/_content_manager/policy |
| Rules | RestPostRuleAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/rules |
RestPutRuleAction | PUT | /_plugins/_content_manager/rules/{id} | |
RestDeleteRuleAction | DELETE | /_plugins/_content_manager/rules/{id} | |
| Decoders | RestPostDecoderAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/decoders |
RestPutDecoderAction | PUT | /_plugins/_content_manager/decoders/{id} | |
RestDeleteDecoderAction | DELETE | /_plugins/_content_manager/decoders/{id} | |
| Integrations | RestPostIntegrationAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/integrations |
RestPutIntegrationAction | PUT | /_plugins/_content_manager/integrations/{id} | |
RestDeleteIntegrationAction | DELETE | /_plugins/_content_manager/integrations/{id} | |
| KVDBs | RestPostKvdbAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs |
RestPutKvdbAction | PUT | /_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs/{id} | |
RestDeleteKvdbAction | DELETE | /_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs/{id} | |
| Promote | RestPostPromoteAction | POST | /_plugins/_content_manager/promote |
RestGetPromoteAction | GET | /_plugins/_content_manager/promote |
Class Hierarchy
The REST handlers follow a Template Method pattern through a three-level abstract class hierarchy:
BaseRestHandler
├── AbstractContentAction
│ ├── AbstractCreateAction
│ │ ├── RestPostRuleAction
│ │ ├── RestPostDecoderAction
│ │ ├── RestPostIntegrationAction
│ │ └── RestPostKvdbAction
│ ├── AbstractUpdateAction
│ │ ├── RestPutRuleAction
│ │ ├── RestPutDecoderAction
│ │ ├── RestPutIntegrationAction
│ │ └── RestPutKvdbAction
│ └── AbstractDeleteAction
│ ├── RestDeleteRuleAction
│ ├── RestDeleteDecoderAction
│ ├── RestDeleteIntegrationAction
│ └── RestDeleteKvdbAction
├── RestPutPolicyAction
├── RestGetSubscriptionAction
├── RestPostSubscriptionAction
├── RestDeleteSubscriptionAction
├── RestPostUpdateAction
├── RestPostLogtestAction
├── RestPostPromoteAction
└── RestGetPromoteAction
AbstractContentAction
Base class for all content CUD actions. It:
- Overrides
prepareRequest()fromBaseRestHandler. - Initializes shared services:
SpaceService,SecurityAnalyticsService,IntegrationService. - Validates that a Draft policy exists before executing any content action.
- Delegates to the abstract
executeRequest()method for concrete logic.
AbstractCreateAction
Handles POST requests to create new resources. The executeRequest() workflow:
- Validate request body — ensures the request has content and valid JSON.
- Validate payload structure — checks for required
resourcekey and optionalintegrationkey. - Resource-specific validation — delegates to
validatePayload()(abstract). Concrete handlers check required fields, duplicate titles, and parent integration existence. - Generate ID and metadata — creates a UUID, sets
dateandmodifiedtimestamps, defaultsenabledtotrue. - External sync — delegates to
syncExternalServices()(abstract). Typically upserts the resource in SAP or validates via the Engine. - Index — wraps the resource in the CTI document structure and indexes it in the Draft space.
- Link to parent — delegates to
linkToParent()(abstract). Usually adds the new resource ID to a parent integration’s resource list. - Update hash — recalculates the Draft space policy hash via
SpaceService.
Returns 201 Created with the new resource UUID on success.
AbstractUpdateAction
Handles PUT requests to update existing resources. The executeRequest() workflow:
- Validate ID — checks the path parameter is present and correctly formatted.
- Check existence and space — verifies the resource exists and belongs to the Draft space.
- Parse and validate payload — same structural checks as create.
- Resource-specific validation — delegates to
validatePayload()(abstract). - Update timestamps — sets
modifiedtimestamp. Preserves immutable fields (creation date, author) from the existing document. - External sync — delegates to
syncExternalServices()(abstract). - Re-index — overwrites the document in the index.
- Update hash — recalculates the Draft space hash.
Returns 200 OK with the resource UUID on success.
AbstractDeleteAction
Handles DELETE requests. The executeRequest() workflow:
- Validate ID — checks format and presence.
- Check existence and space — resource must exist in Draft space.
- Pre-delete validation — delegates to
validateDelete()(optional override). Can prevent deletion if dependent resources exist. - External sync — delegates to
deleteExternalServices()(abstract). Removes from SAP. Handles 404 gracefully. - Unlink from parent — delegates to
unlinkFromParent()(abstract). Removes the resource ID from the parent integration’s list. - Delete from index — removes the document.
- Update hash — recalculates the Draft space hash.
Returns 200 OK with the resource UUID on success.
Engine Communication
The plugin communicates with the Wazuh Engine via a Unix Domain Socket for validation and promotion of content.
EngineSocketClient
Located at: engine/client/EngineSocketClient.java
- Connects to the socket at
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/engine/sockets/engine-api.sock. - Sends HTTP-over-UDS requests: builds a standard HTTP/1.1 request string (method, headers, JSON body) and writes it to the socket channel.
- Each request opens a new
SocketChannel(usingStandardProtocolFamily.UNIX) that is closed after the response is read. - Parses the HTTP response, extracting the status code and JSON body.
EngineService Interface
Defines the Engine operations:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
logtest(JsonNode log) | Forwards a log test payload to the Engine |
validate(JsonNode resource) | Validates a resource payload |
promote(JsonNode policy) | Validates a full policy for promotion |
validateResource(String type, JsonNode resource) | Wraps a resource with its type and delegates to validate() |
EngineServiceImpl
Implementation using EngineSocketClient. Maps methods to Engine API endpoints:
| Method | Engine Endpoint | HTTP Method |
|---|---|---|
logtest() | /logtest | POST |
validate() | /content/validate/resource | POST |
promote() | /content/validate/policy | POST |
Space Model
Resources live in spaces that represent their lifecycle stage. The Space enum defines four spaces:
| Space | Description |
|---|---|
STANDARD | Production-ready CTI resources from the upstream catalog |
CUSTOM | User-created resources that have been promoted to production |
DRAFT | Resources under development — all user edits happen here |
TEST | Intermediate space for validation before production |
Promotion Flow
Spaces promote in a fixed chain:
DRAFT → TEST → CUSTOM
The Space.promote() method returns the next space in the chain. STANDARD and CUSTOM spaces cannot be promoted further.
SpaceService
Located at: cti/catalog/service/SpaceService.java
Manages space-related operations:
getSpaceResources(spaceName)— Fetches all resources (document IDs and hashes) from all managed indices for a given space.promoteSpace(indexName, resources, targetSpace)— Copies documents from one space to another via bulk indexing, updating thespace.namefield.calculateAndUpdate(targetSpaces)— Recalculates the aggregate SHA-256 hash for each policy in the given spaces. The hash is computed by concatenating hashes of the policy and all its linked resources (integrations, decoders, KVDBs, rules).buildEnginePayload(...)— Assembles the full policy payload (policy + all resources from target space with modifications applied) for Engine validation during promotion.deleteResources(indexName, ids, targetSpace)— Bulk-deletes resources from a target space.
Document Structure
Every resource document follows this envelope structure:
{
"document": {
"id": "<uuid>",
"title": "...",
"date": "2026-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"modified": "2026-01-15T00:00:00Z",
"enabled": true
},
"hash": {
"sha256": "abc123..."
},
"space": {
"name": "draft",
"hash": {
"sha256": "xyz789..."
}
}
}
Content Synchronization Pipeline
Overview
sequenceDiagram
participant Scheduler as JobScheduler/RestAction
participant SyncJob as CatalogSyncJob
participant Synchronizer as ConsumerRulesetService
participant ConsumerSvc as ConsumerService
participant CTI as External CTI API
participant Snapshot as SnapshotService
participant Update as UpdateService
participant Indices as Content Indices
participant SAP as SecurityAnalyticsServiceImpl
Scheduler->>SyncJob: Trigger Execution
activate SyncJob
SyncJob->>Synchronizer: synchronize()
Synchronizer->>ConsumerSvc: getLocalConsumer() / getRemoteConsumer()
ConsumerSvc->>CTI: Fetch Metadata
ConsumerSvc-->>Synchronizer: Offsets & Metadata
alt Local Offset == 0 (Initialization)
Synchronizer->>Snapshot: initialize(remoteConsumer)
Snapshot->>CTI: Download Snapshot ZIP
Snapshot->>Indices: Bulk Index Content (Rules/Integrations/etc.)
Snapshot-->>Synchronizer: Done
else Local Offset < Remote Offset (Update)
Synchronizer->>Update: update(localOffset, remoteOffset)
Update->>CTI: Fetch Changes
Update->>Indices: Apply JSON Patches
Update-->>Synchronizer: Done
end
opt Changes Applied (onSyncComplete)
Synchronizer->>Indices: Refresh Indices
Synchronizer->>SAP: upsertIntegration(doc)
loop For each Integration
SAP->>SAP: WIndexIntegrationAction
end
Synchronizer->>SAP: upsertRule(doc)
loop For each Rule
SAP->>SAP: WIndexRuleAction
end
Synchronizer->>SAP: upsertDetector(doc)
loop For each Integration
SAP->>SAP: WIndexDetectorAction
end
Synchronizer->>Synchronizer: calculatePolicyHash()
end
deactivate SyncJob
Initialization Phase
When local_offset = 0:
- Downloads a ZIP snapshot from the CTI API.
- Extracts and parses JSON files for each content type.
- Bulk-indexes content into respective indices.
- Registers all content with the Security Analytics Plugin via
SecurityAnalyticsServiceImpl.
Update Phase
When local_offset > 0 and local_offset < remote_offset:
- Fetches changes in batches from the CTI API.
- Applies JSON Patch operations (add, update, delete).
- Pushes changes to the Security Analytics Plugin via
SecurityAnalyticsServiceImpl. - Updates the local offset.
Post-Synchronization Phase
- Refreshes all content indices.
- Upserts integrations, rules, and detectors into the Security Analytics Plugin via
SecurityAnalyticsServiceImpl. - Recalculates SHA-256 hashes for policy integrity verification.
Error Handling
If a critical error or data corruption is detected, the system resets local_offset to 0, triggering a full snapshot re-initialization on the next run.
Configuration Settings
Settings are defined in PluginSettings and configured in opensearch.yml:
| Setting | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
plugins.content_manager.cti.api | https://cti-pre.wazuh.com/api/v1 | Base URL for the Wazuh CTI API |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.sync_interval | 60 | Sync interval in minutes (1–1440) |
plugins.content_manager.max_items_per_bulk | 25 | Max documents per bulk request (10–25) |
plugins.content_manager.max_concurrent_bulks | 5 | Max concurrent bulk requests (1–5) |
plugins.content_manager.client.timeout | 10 | Timeout in seconds for HTTP/indexing (10–50) |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_start | true | Trigger sync on plugin start |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_schedule | true | Enable periodic sync job |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.content.context | development_0.0.3 | CTI content context identifier |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.content.consumer | development_0.0.3_test | CTI content consumer identifier |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.create_detectors | true | Enable automatic detector creation |
REST API URIs
All endpoints are under /_plugins/_content_manager. The URI constants are defined in PluginSettings:
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
PLUGINS_BASE_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager |
SUBSCRIPTION_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/subscription |
UPDATE_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/update |
LOGTEST_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/logtest |
RULES_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/rules |
DECODERS_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/decoders |
INTEGRATIONS_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/integrations |
KVDBS_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs |
PROMOTE_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/promote |
POLICY_URI | /_plugins/_content_manager/policy |
REST API Reference
The full API is defined in openapi.yml.
Logtest
The Indexer acts as a proxy between the UI and the Engine. POST /logtest accepts the payload and forwards it to the Engine via UDS. No validation is performed. If the Engine responds, its response is returned directly. If the Engine is unreachable, a 500 error is returned.
A testing policy must be loaded in the Engine for logtest to work. Load a policy via the policy promotion endpoint.
---
title: Logtest execution
---
sequenceDiagram
actor User
participant UI
participant Indexer
participant Engine
User->>UI: run logtest
UI->>Indexer: POST /logtest
Indexer->>Engine: POST /logtest (via UDS)
Engine-->>Indexer: response
Indexer-->>UI: response
Content RUD (Rules, Decoders, Integrations, KVDBs)
All four resource types follow the same patterns via the abstract class hierarchy:
Create (POST):
sequenceDiagram
actor User
participant Indexer
participant Engine/SAP as Engine or SAP
participant ContentIndex
participant IntegrationIndex
User->>Indexer: POST /_plugins/_content_manager/{resource_type}
Indexer->>Indexer: Validate payload, generate UUID, timestamps
Indexer->>Engine/SAP: Sync (validate/upsert)
Engine/SAP-->>Indexer: OK
Indexer->>ContentIndex: Index in Draft space
Indexer->>IntegrationIndex: Link to parent integration
Indexer-->>User: 201 Created + UUID
Update (PUT):
sequenceDiagram
actor User
participant Indexer
participant ContentIndex
participant Engine/SAP as Engine or SAP
User->>Indexer: PUT /_plugins/_content_manager/{resource_type}/{id}
Indexer->>ContentIndex: Check exists + is in Draft space
Indexer->>Indexer: Validate, preserve metadata, update timestamps
Indexer->>Engine/SAP: Sync (validate/upsert)
Indexer->>ContentIndex: Re-index document
Indexer-->>User: 200 OK + UUID
Delete (DELETE):
sequenceDiagram
actor User
participant Indexer
participant ContentIndex
participant Engine/SAP as Engine or SAP
participant IntegrationIndex
User->>Indexer: DELETE /_plugins/_content_manager/{resource_type}/{id}
Indexer->>ContentIndex: Check exists + is in Draft space
Indexer->>Engine/SAP: Delete from external service
Indexer->>IntegrationIndex: Unlink from parent
Indexer->>ContentIndex: Delete document
Indexer-->>User: 200 OK + UUID
Draft Policy Update
flowchart TD
UI[UI] -->|PUT /policy| Indexer
Indexer -->|Validate| Check{Valid content?}
Check -->|No| Error[400 Error]
Check -->|Yes| Parse[Parse & validate fields]
Parse --> Store[Index to .cti-policies in Draft space]
Store --> OK[200 OK]
Policy Schema
The .cti-policies index stores policy configurations. See the Policy document structure above for the envelope format.
Policy document fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | keyword | Unique identifier |
title | keyword | Human-readable name |
date | date | Creation timestamp |
modified | date | Last modification timestamp |
root_decoder | keyword | Root decoder for event processing |
integrations | keyword[] | Active integration IDs |
filters | keyword[] | Filter UUIDs |
enrichments | keyword[] | Enrichment types (file, domain-name, ip, url, geo) |
author | keyword | Policy author |
description | text | Brief description |
documentation | keyword | Documentation link |
references | keyword[] | External reference URLs |
Debugging
Check Consumer Status
GET /.cti-consumers/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} }
}
Check Content by Space
GET /.cti-rules/_search
{
"query": { "term": { "space.name": "draft" } },
"size": 10
}
Monitor Plugin Logs
tail -f var/log/wazuh-indexer/wazuh-cluster.log | grep -E "ContentManager|CatalogSyncJob|SnapshotServiceImpl|UpdateServiceImpl|AbstractContentAction"
Important Notes
- The plugin only runs on cluster manager nodes.
- CTI API must be accessible for content synchronization.
- All user content CUD operations require a Draft policy to exist.
- The Engine socket must be available at the configured path for logtest, validation, and promotion.
- Offset-based synchronization ensures no content is missed.
🧪 Testing
The plugin includes integration tests defined in the tests/content-manager directory. These tests cover various scenarios for managing integrations, decoders, rules, and KVDBs through the REST API.
01 - Integrations: Create Integration (9 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully create an integration |
| 2 | Create an integration with the same title as an existing integration |
| 3 | Create an integration with missing title |
| 4 | Create an integration with missing author |
| 5 | Create an integration with missing category |
| 6 | Create an integration with an explicit id in the resource |
| 7 | Create an integration with missing resource object |
| 8 | Create an integration with empty body |
| 9 | Create an integration without authentication |
01 - Integrations: Update Integration (8 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully update an integration |
| 2 | Update an integration changing its title to a title that already exists in draft space |
| 3 | Update an integration with missing required fields |
| 4 | Update an integration that does not exist |
| 5 | Update an integration with an invalid UUID |
| 6 | Update an integration with an id in the request body |
| 7 | Update an integration attempting to add/remove dependency lists |
| 8 | Update an integration without authentication |
01 - Integrations: Delete Integration (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully delete an integration with no attached resources |
| 2 | Delete an integration that has attached resources |
| 3 | Delete an integration that does not exist |
| 4 | Delete an integration with an invalid UUID |
| 5 | Delete an integration without providing an ID |
| 6 | Delete an integration not in draft space |
| 7 | Delete an integration without authentication |
02 - Decoders: Create Decoder (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully create a decoder |
| 2 | Create a decoder without an integration reference |
| 3 | Create a decoder with an explicit id in the resource |
| 4 | Create a decoder with an integration not in draft space |
| 5 | Create a decoder with missing resource object |
| 6 | Create a decoder with empty body |
| 7 | Create a decoder without authentication |
02 - Decoders: Update Decoder (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully update a decoder |
| 2 | Update a decoder that does not exist |
| 3 | Update a decoder with an invalid UUID |
| 4 | Update a decoder not in draft space |
| 5 | Update a decoder with missing resource object |
| 6 | Update a decoder with empty body |
| 7 | Update a decoder without authentication |
02 - Decoders: Delete Decoder (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully delete a decoder |
| 2 | Delete a decoder that does not exist |
| 3 | Delete a decoder with an invalid UUID |
| 4 | Delete a decoder not in draft space |
| 5 | Delete a decoder without providing an ID |
| 6 | Delete a decoder without authentication |
| 7 | Verify decoder is removed from index after deletion |
03 - Rules: Create Rule (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully create a rule |
| 2 | Create a rule with missing title |
| 3 | Create a rule without an integration reference |
| 4 | Create a rule with an explicit id in the resource |
| 5 | Create a rule with an integration not in draft space |
| 6 | Create a rule with empty body |
| 7 | Create a rule without authentication |
03 - Rules: Update Rule (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully update a rule |
| 2 | Update a rule with missing title |
| 3 | Update a rule that does not exist |
| 4 | Update a rule with an invalid UUID |
| 5 | Update a rule not in draft space |
| 6 | Update a rule with empty body |
| 7 | Update a rule without authentication |
03 - Rules: Delete Rule (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully delete a rule |
| 2 | Delete a rule that does not exist |
| 3 | Delete a rule with an invalid UUID |
| 4 | Delete a rule not in draft space |
| 5 | Delete a rule without providing an ID |
| 6 | Delete a rule without authentication |
| 7 | Verify rule is removed from index after deletion |
04 - KVDBs: Create KVDB (9 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully create a KVDB |
| 2 | Create a KVDB with missing title |
| 3 | Create a KVDB with missing author |
| 4 | Create a KVDB with missing content |
| 5 | Create a KVDB without an integration reference |
| 6 | Create a KVDB with an explicit id in the resource |
| 7 | Create a KVDB with an integration not in draft space |
| 8 | Create a KVDB with empty body |
| 9 | Create a KVDB without authentication |
04 - KVDBs: Update KVDB (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully update a KVDB |
| 2 | Update a KVDB with missing required fields |
| 3 | Update a KVDB that does not exist |
| 4 | Update a KVDB with an invalid UUID |
| 5 | Update a KVDB not in draft space |
| 6 | Update a KVDB with empty body |
| 7 | Update a KVDB without authentication |
04 - KVDBs: Delete KVDB (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully delete a KVDB |
| 2 | Delete a KVDB that does not exist |
| 3 | Delete a KVDB with an invalid UUID |
| 4 | Delete a KVDB not in draft space |
| 5 | Delete a KVDB without providing an ID |
| 6 | Delete a KVDB without authentication |
| 7 | Verify KVDB is removed from index after deletion |
05 - Policy: Policy Initialization (6 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | The “.cti-policies” index exists |
| 2 | Exactly four policy documents exist (one per space) |
| 3 | Standard policy has a different document ID than draft/test/custom |
| 4 | Draft, test, and custom policies start with empty integrations and root_decoder |
| 5 | Each policy document contains the expected structure |
| 6 | Each policy has a valid SHA-256 hash |
05 - Policy: Update Draft Policy (12 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully update the draft policy |
| 2 | Update policy with missing type field |
| 3 | Update policy with wrong type value |
| 4 | Update policy with missing resource object |
| 5 | Update policy with missing required fields in resource |
| 6 | Update policy attempting to add an integration to the list |
| 7 | Update policy attempting to remove an integration from the list |
| 8 | Update policy with reordered integrations list (allowed) |
| 9 | Update policy with empty body |
| 10 | Update policy without authentication |
| 11 | Verify policy changes are NOT reflected in test space until promotion |
| 12 | Verify policy changes are reflected in test space after promotion |
06 - Log Test (4 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully test a log event |
| 2 | Send log test with empty body |
| 3 | Send log test with invalid JSON |
| 4 | Send log test without authentication |
07 - Promote: Preview Promotion (7 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Preview promotion from draft to test |
| 2 | Preview promotion from test to custom |
| 3 | Preview promotion with missing space parameter |
| 4 | Preview promotion with empty space parameter |
| 5 | Preview promotion with invalid space value |
| 6 | Preview promotion from custom (not allowed) |
| 7 | Preview promotion without authentication |
07 - Promote: Execute Promotion (18 scenarios)
| # | Scenario |
|---|---|
| 1 | Successfully promote from draft to test |
| 2 | Verify resources exist in test space after draft to test promotion |
| 3 | Verify promoted resources exist in both draft and test spaces |
| 4 | Verify test space hash is regenerated after draft to test promotion |
| 5 | Verify promoted resource hashes match between draft and test spaces |
| 6 | Verify deleting a decoder in draft does not affect promoted test space |
| 7 | Successfully promote from test to custom |
| 8 | Verify resources exist in custom space after test to custom promotion |
| 9 | Verify promoted resources exist in both test and custom spaces |
| 10 | Verify custom space hash is regenerated after test to custom promotion |
| 11 | Verify promoted resource hashes match between test and custom spaces |
| 12 | Promote from custom (not allowed) |
| 13 | Promote with invalid space |
| 14 | Promote with missing changes object |
| 15 | Promote with incomplete changes (missing required resource arrays) |
| 16 | Promote with non-update operation on policy |
| 17 | Promote with empty body |
| 18 | Promote without authentication |
Related Documentation
Tutorial: Adding a REST Endpoint to the Content Manager Plugin
This tutorial walks through adding a new REST endpoint to the Content Manager plugin, using a concrete example: a GET endpoint to retrieve a single rule by ID.
By the end, you will have a working GET /_plugins/_content_manager/rules/{id} endpoint that fetches a rule document from the .cti-rules index.
Prerequisites
- Development environment set up (see Setup)
- The project compiles:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:compileJava
Step 1: Add the URI Constant
If your endpoint uses a new base URI, add it to PluginSettings. In this case, rules already have RULES_URI, and our GET endpoint uses the same base path with an {id} parameter, so no changes are needed.
The existing constant in PluginSettings.java:
public static final String RULES_URI = PLUGINS_BASE_URI + "/rules";
Our endpoint will match /_plugins/_content_manager/rules/{id} using the same base URI.
Step 2: Create the Handler Class
Create a new file at:
plugins/content-manager/src/main/java/com/wazuh/contentmanager/rest/service/RestGetRuleAction.java
package com.wazuh.contentmanager.rest.service;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger;
import org.opensearch.core.rest.RestStatus;
import org.opensearch.rest.BaseRestHandler;
import org.opensearch.rest.BytesRestResponse;
import org.opensearch.rest.NamedRoute;
import org.opensearch.rest.RestRequest;
import org.opensearch.transport.client.node.NodeClient;
import java.util.List;
import com.wazuh.contentmanager.cti.catalog.index.ContentIndex;
import com.wazuh.contentmanager.settings.PluginSettings;
import com.wazuh.contentmanager.utils.Constants;
/**
* GET /_plugins/_content_manager/rules/{id}
*
* Retrieves a single rule document by its ID from the .cti-rules index.
*/
public class RestGetRuleAction extends BaseRestHandler {
private static final Logger log = LogManager.getLogger(RestGetRuleAction.class);
private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();
// A short identifier for log output and debugging.
private static final String ENDPOINT_NAME = "content_manager_rule_get";
// A unique name used by OpenSearch's named route system for access control.
private static final String ENDPOINT_UNIQUE_NAME = "plugin:content_manager/rule_get";
@Override
public String getName() {
return ENDPOINT_NAME;
}
/**
* Define the route. The {id} path parameter is automatically extracted
* by OpenSearch and available via request.param("id").
*/
@Override
public List<Route> routes() {
return List.of(
new NamedRoute.Builder()
.path(PluginSettings.RULES_URI + "/{id}")
.method(RestRequest.Method.GET)
.uniqueName(ENDPOINT_UNIQUE_NAME)
.build());
}
/**
* Prepare and execute the request. This method is called by the
* OpenSearch REST framework for each incoming request.
*
* @param request the incoming REST request
* @param client the node client for index operations
* @return a RestChannelConsumer that writes the response
*/
@Override
protected RestChannelConsumer prepareRequest(RestRequest request, NodeClient client) {
// Extract the {id} path parameter.
String id = request.param(Constants.KEY_ID);
return channel -> {
try {
// Validate the ID parameter is present.
if (id == null || id.isBlank()) {
channel.sendResponse(new BytesRestResponse(
RestStatus.BAD_REQUEST,
"application/json",
"{\"error\": \"Missing required parameter: id\"}"));
return;
}
// Use ContentIndex to retrieve the document.
ContentIndex index = new ContentIndex(client, Constants.INDEX_RULES, null);
JsonNode document = index.getDocument(id);
if (document == null) {
channel.sendResponse(new BytesRestResponse(
RestStatus.NOT_FOUND,
"application/json",
"{\"error\": \"Rule not found: " + id + "\"}"));
return;
}
// Return the document as JSON.
String responseBody = MAPPER.writeValueAsString(document);
channel.sendResponse(new BytesRestResponse(
RestStatus.OK,
"application/json",
responseBody));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to retrieve rule [{}]: {}", id, e.getMessage(), e);
channel.sendResponse(new BytesRestResponse(
RestStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,
"application/json",
"{\"error\": \"Internal server error: " + e.getMessage() + "\"}"));
}
};
}
}
Key Concepts
getName()— Returns a short identifier used in logs and debugging.routes()— Defines the HTTP method and URI pattern. UsesNamedRoute.Builderwhich requires auniqueNamefor OpenSearch’s access control system.prepareRequest()— The core method. Returns aRestChannelConsumerlambda that executes asynchronously and writes the response to the channel.- Path parameters —
{id}in the route path is automatically parsed. Access it withrequest.param("id").
Step 3: Register the Handler
Open ContentManagerPlugin.java and add the new handler to getRestHandlers():
@Override
public List<RestHandler> getRestHandlers(
Settings settings,
RestController restController,
ClusterSettings clusterSettings,
IndexScopedSettings indexScopedSettings,
SettingsFilter settingsFilter,
IndexNameExpressionResolver indexNameExpressionResolver,
Supplier<DiscoveryNodes> nodesInCluster) {
return List.of(
// ... existing handlers ...
// Rule endpoints
new RestPostRuleAction(),
new RestPutRuleAction(),
new RestDeleteRuleAction(),
new RestGetRuleAction(), // <-- Add the new handler
// ... remaining handlers ...
);
}
Make sure to add the import at the top of the file:
import com.wazuh.contentmanager.rest.service.RestGetRuleAction;
Step 4: Build and Verify
Compile the plugin to check for errors:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:compileJava
If compilation succeeds, run the full build (including tests):
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:build
Step 5: Test the Endpoint
Manual Testing
Start a local cluster (see tools/test-cluster) and test:
# Create a rule first (so there's something to fetch)
curl -X POST "https://localhost:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/rules" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-u admin:admin --insecure \
-d '{
"integration": "<integration-id>",
"resource": {
"title": "Test Rule"
}
}'
# The response returns the UUID. Use it to fetch:
curl -X GET "https://localhost:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/rules/<uuid>" \
-u admin:admin --insecure
Writing a Unit Test
Create a test file at:
plugins/content-manager/src/test/java/com/wazuh/contentmanager/rest/service/RestGetRuleActionTests.java
At minimum, test that getName() and routes() return expected values:
package com.wazuh.contentmanager.rest.service;
import org.opensearch.rest.RestRequest;
import org.opensearch.test.OpenSearchTestCase;
public class RestGetRuleActionTests extends OpenSearchTestCase {
public void testGetName() {
RestGetRuleAction action = new RestGetRuleAction();
assertEquals("content_manager_rule_get", action.getName());
}
public void testRoutes() {
RestGetRuleAction action = new RestGetRuleAction();
assertEquals(1, action.routes().size());
assertEquals(RestRequest.Method.GET, action.routes().get(0).getMethod());
assertTrue(action.routes().get(0).getPath().contains("/rules/{id}"));
}
}
Run:
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:test
Summary
To add a new REST endpoint to the Content Manager plugin:
- Create the handler class — Extend
BaseRestHandler(for simple endpoints) or one of the abstract classes (AbstractCreateAction,AbstractUpdateAction,AbstractDeleteAction) for standard CUD. - Define routes — Use
NamedRoute.Builderwith a unique name. - Implement logic — Override
prepareRequest()(orexecuteRequest()if extending the abstract hierarchy). - Register — Add the instance to
ContentManagerPlugin.getRestHandlers(). - Build and test —
./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:compileJavathen./gradlew :wazuh-indexer-content-manager:test.
For content CUD endpoints that need Draft space validation, Engine sync, and hash updates, extend AbstractContentAction or one of its children instead of BaseRestHandler directly.
Description
The Wazuh Indexer is a highly scalable, full-text search and analytics engine built over OpenSearch. It serves as the central data store for the Wazuh platform, indexing and storing security alerts, events, vulnerability data, and system inventory generated by Wazuh Agents and the Wazuh Server. It provides near real-time search and analytics capabilities, enabling security teams to investigate threats, monitor compliance, and gain visibility into their infrastructure.
The Wazuh Indexer can be deployed as a single-node instance for development and small environments, or as a multi-node cluster for production workloads requiring high availability and horizontal scalability.
Core Concepts
The Wazuh Indexer stores data as JSON documents. Each document contains a set of fields (keys) mapped to values — strings, numbers, booleans, dates, arrays, nested objects, and more.
An index is a collection of related documents. For time-series data such as alerts and events, the Wazuh Indexer uses data streams backed by rolling indices with automatic lifecycle management.
Documents are distributed across shards, which are spread across cluster nodes. This distribution provides redundancy against hardware failures and allows query throughput to scale as nodes are added.
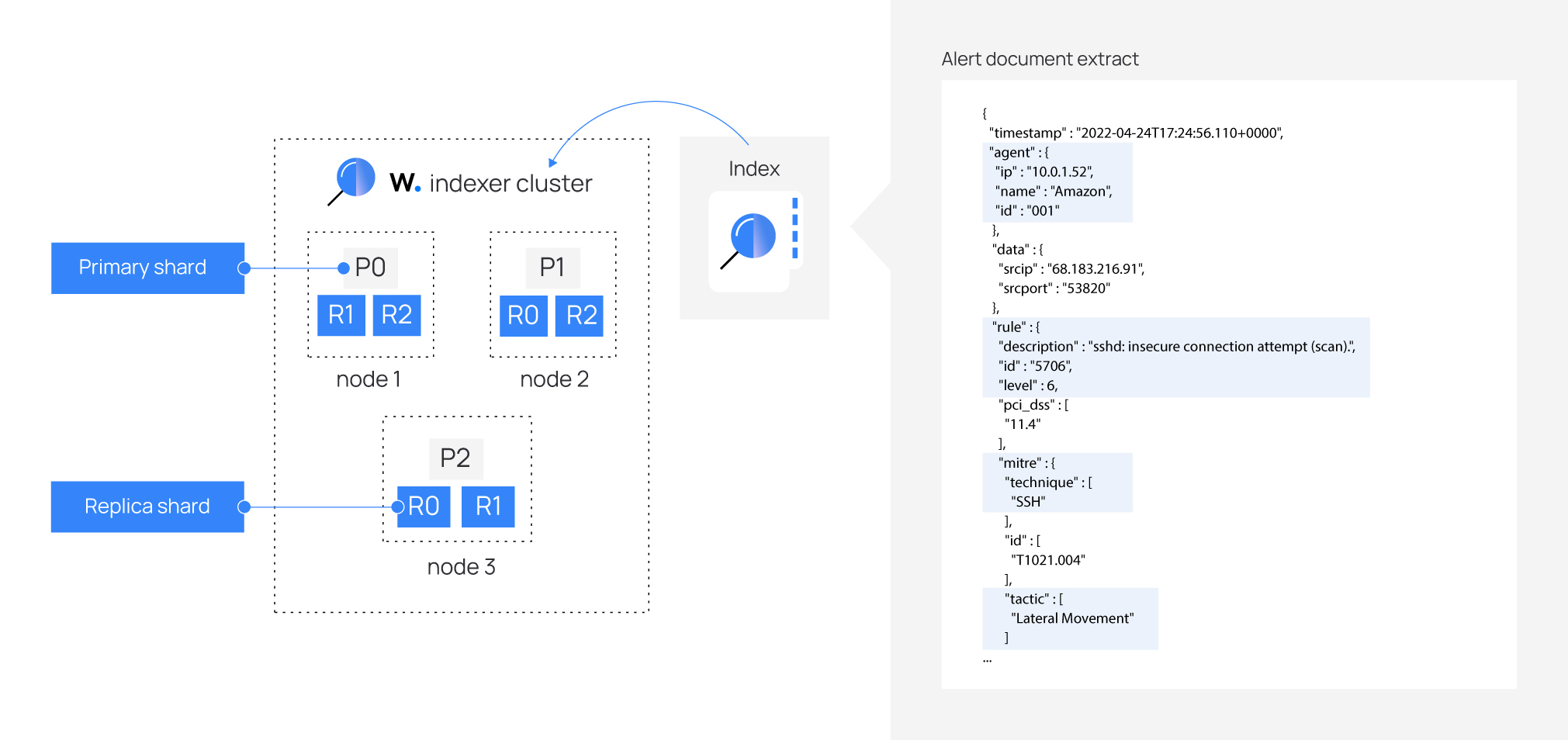
Bundled Plugins
The Wazuh Indexer ships with four purpose-built plugins that extend OpenSearch for security monitoring use cases:
Setup Plugin
The Setup plugin initializes the indexer environment on cluster startup. It creates all required index templates, Index State Management (ISM) policies, data streams, and internal state indices. This ensures the correct schema and lifecycle rules are in place before any data is ingested. The Setup plugin defines the Wazuh Common Schema — the standardized field mappings used across all Wazuh indices.
Content Manager Plugin
The Content Manager plugin is responsible for keeping the Wazuh detection content up to date. It synchronizes rules, decoders, integrations, key-value databases (KVDBs), and Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) from the Wazuh Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) API. It also provides a REST API for managing user-generated content — custom rules, decoders, and integrations that can be drafted, tested, and promoted to the active Wazuh Engine configuration.
The Content Manager communicates with the Wazuh Engine through a Unix socket to execute log tests, validate configurations, and reload content. See Content Manager for details.
Security Plugin
The Security plugin provides role-based access control (RBAC), user authentication, and TLS encryption for both the REST API and inter-node transport layers. It ships with predefined roles tailored to Wazuh operations, allowing administrators to control which users can access specific indices, APIs, and dashboards.
Reporting Plugin
The Reporting plugin enables the generation of PDF and CSV reports from Wazuh Dashboard visualizations and saved searches. Reports can be triggered on demand or scheduled for periodic delivery.
Data Storage
The Wazuh Indexer organizes data into purpose-specific indices:
| Index pattern | Description |
|---|---|
wazuh-events-* | Raw security events from monitored endpoints |
wazuh-states-* | System state and inventory data (vulnerabilities, packages, ports, etc.) |
wazuh-statistics-* | Operational statistics for the Wazuh cluster |
.cti-* | Content Manager system indices for CTI content |
For a complete list of indices and their schemas, see the Setup Plugin documentation.
Integration with the Wazuh Platform
The Wazuh Indexer integrates with:
- Wazuh Server / Engine: Receives analyzed events and alerts; the Content Manager syncs detection content back to the Engine.
- Wazuh Dashboard: An OpenSearch Dashboards fork that provides the web UI for searching, visualizing, and managing Wazuh data.
- Wazuh Agents: Collect endpoint data that ultimately flows into the Indexer after processing by the Engine.
The Indexer exposes a standard REST API compatible with the OpenSearch API, so existing OpenSearch tools, clients, and integrations work with the Wazuh Indexer out of the box.
Architecture
The Wazuh Indexer is built on top of OpenSearch and extends it with a set of purpose-built plugins that provide security event indexing, content management, access control, and reporting capabilities.
Component Overview
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Wazuh Indexer │
│ │
│ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌─────────┐ │
│ │ Setup Plugin │ │ Content Manager │ │ Security │ │Reporting│ │
│ │ │ │ Plugin │ │ Plugin │ │ Plugin │ │
│ └──────┬───────┘ └────────┬─────────┘ └────┬─────┘ └───┬─────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ ┌──────┴────────┐ ┌──────┴───────────┐ ┌──┴───────┐ │ │
│ │Index Templates│ │ CTI API Client │ │ RBAC & │ │ │
│ │ISM Policies │ │ Engine Client │ │ Access │ │ │
│ │Stream Indices │ │ Job Scheduler │ │ Control │ │ │
│ │State Indices │ │ Space Service │ └──────────┘ │ │
│ └───────────────┘ └───────┬──────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ ┌─────────┴──────────┐ │ │
│ │ System Indices │ │ │
│ │ .cti-consumers │ │ │
│ │ .cti-rules │ │ │
│ │ .cti-decoders │ │ │
│ │ .cti-integrations │ │ │
│ │ .cti-kvdbs │ │ │
│ │ .cti-policies │ │ │
│ │ .cti-iocs │ │ │
│ └────────────────────┘ │ │
└─────────────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────┼────────┘
│ Unix Socket │
┌───────┴────────┐ ┌──────┴───────┐
│ Wazuh Engine │ │ Wazuh │
│ (Analysis & │ │ Dashboard │
│ Detection) │ │ (UI) │
└────────────────┘ └──────────────┘
Plugins
Setup Plugin
The Setup plugin initializes the Wazuh Indexer environment when the cluster starts. It is responsible for:
- Index templates: Defines the mappings and settings for all Wazuh indices (alerts, events, statistics, vulnerabilities, etc.).
- ISM (Index State Management) policies: Configures lifecycle policies for automatic rollover, deletion, and retention of time-series indices.
- Data streams: Creates the initial data stream indices that receive incoming event data.
- State indices: Sets up internal indices used by other Wazuh components to track operational state.
The Setup plugin runs once during cluster initialization and ensures the required infrastructure is in place before other plugins begin operating.
Content Manager Plugin
The Content Manager is the most feature-rich plugin. It handles:
- CTI synchronization: Periodically fetches threat intelligence content (rules, decoders, integrations, KVDBs, IoCs) from the Wazuh CTI API. On first run, it downloads a full snapshot; subsequent runs apply incremental patches.
- User-generated content: Provides a REST API for creating, updating, and deleting custom decoders, rules, integrations, and KVDBs in a draft space.
- Promotion workflow: Changes made in the draft space can be previewed and promoted to the Wazuh Engine for activation.
- Engine communication: Communicates with the Wazuh Engine via a Unix socket for logtest execution, content validation, and configuration reload.
- Policy management: Manages the Engine routing policy that controls how events are processed.
See Content Manager for full details.
Security Plugin
The Security plugin extends OpenSearch’s security capabilities for Wazuh-specific needs:
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Defines predefined roles and permissions for Wazuh operations.
- User management: Provides APIs and configuration for managing users and their access levels.
- TLS/SSL: Handles transport and REST layer encryption.
Reporting Plugin
The Reporting plugin enables on-demand and scheduled report generation from the Wazuh Dashboard, producing PDF or CSV exports of dashboards and saved searches.
Data Flow
- Wazuh Agents collect security events from monitored endpoints and forward them to the Wazuh Server.
- The Wazuh Engine on the server analyzes events using rules and decoders, then forwards alerts and events to the Wazuh Indexer via the Indexer API.
- The Setup Plugin ensures the correct index templates, data streams, and lifecycle policies exist.
- The Content Manager Plugin keeps the Engine’s detection content up to date by synchronizing with the CTI API and managing user customizations.
- The Wazuh Dashboard queries the Indexer to visualize alerts, events, and security analytics.
Compatibility
Supported operating systems
We aim to support as many operating systems as OpenSearch does. Wazuh indexer should work on many Linux distributions, but we only test a handful. The following table lists the operating system versions that we currently support.
For 5.0.0 and above, we support the operating system versions and architectures included in the table below.
| Name | Version | Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat | 8, 9 | x86_64, aarch64 |
| Ubuntu | 22.04, 24.04 | x86_64, aarch64 |
| Amazon Linux | 2, 2023 | x86_64, aarch64 |
| CentOS | 8 | x86_64, aarch64 |
OpenSearch
Currently, Wazuh indexer is using version 3.0.0 of OpenSearch.
Requirements
Hardware recommendations
The Wazuh indexer can be installed as a single-node or as a multi-node cluster.
Hardware recommendations for each node
| Minimum | Recommended | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | RAM (GB) | CPU (cores) | RAM (GB) | CPU (cores) |
| Wazuh indexer | 4 | 2 | 16 | 8 |
Disk space requirements
The amount of data depends on the generated alerts per second (APS). This table details the estimated disk space needed per agent to store 90 days of alerts on a Wazuh indexer server, depending on the type of monitored endpoints.
| Monitored endpoints | APS | Storage in Wazuh indexer (GB/90 days) |
|---|---|---|
| Servers | 0.25 | 3.7 |
| Workstations | 0.1 | 1.5 |
| Network devices | 0.5 | 7.4 |
For example, for an environment with 80 workstations, 10 servers, and 10 network devices, the storage needed on the Wazuh indexer server for 90 days of alerts is 230 GB.
Packages
Please refer to this section for information pertaining to compatibility.
Installation
Installing the Wazuh indexer step by step
Install and configure the Wazuh indexer as a single-node or multi-node cluster, following step-by-step instructions. The installation process is divided into three stages.
-
Certificates creation
-
Nodes installation
-
Cluster initialization
Note You need root user privileges to run all the commands described below.
1. Certificates creation
Generating the SSL certificates
-
Download the
wazuh-certs-tool.shscript and theconfig.ymlconfiguration file. This creates the certificates that encrypt communications between the Wazuh central components.curl -sO https://packages-dev.wazuh.com/5.0/wazuh-certs-tool.sh curl -sO https://packages-dev.wazuh.com/5.0/config.yml -
Edit
./config.ymland replace the node names and IP values with the corresponding names and IP addresses. You need to do this for all Wazuh server, Wazuh indexer, and Wazuh dashboard nodes. Add as many node fields as needed.nodes: # Wazuh indexer nodes indexer: - name: node-1 ip: "<indexer-node-ip>" #- name: node-2 # ip: "<indexer-node-ip>" #- name: node-3 # ip: "<indexer-node-ip>" # Wazuh server nodes # If there is more than one Wazuh server # node, each one must have a node_type server: - name: wazuh-1 ip: "<wazuh-manager-ip>" # node_type: master #- name: wazuh-2 # ip: "<wazuh-manager-ip>" # node_type: worker #- name: wazuh-3 # ip: "<wazuh-manager-ip>" # node_type: worker # Wazuh dashboard nodes dashboard: - name: dashboard ip: "<dashboard-node-ip>"To learn more about how to create and configure the certificates, see the Certificates deployment section.
-
Run
./wazuh-certs-tool.shto create the certificates. For a multi-node cluster, these certificates need to be later deployed to all Wazuh instances in your cluster../wazuh-certs-tool.sh -A -
Compress all the necessary files.
tar -cvf ./wazuh-certificates.tar -C ./wazuh-certificates/ . rm -rf ./wazuh-certificates -
Copy the
wazuh-certificates.tarfile to all the nodes, including the Wazuh indexer, Wazuh server, and Wazuh dashboard nodes. This can be done by using thescputility.
2. Nodes installation
Installing package dependencies
Install the following packages if missing:
Yum
yum install coreutils
APT
apt-get install debconf adduser procps
Adding the Wazuh repository
Yum
-
Import the GPG key.
rpm --import https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH -
Add the repository.
echo -e '[wazuh]\ngpgcheck=1\ngpgkey=https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH\nenabled=1\nname=EL-$releasever - Wazuh\nbaseurl=https://packages.wazuh.com/5.x/yum/\nprotect=1' | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/wazuh.repo
APT
-
Install the following packages if missing.
apt-get install gnupg apt-transport-https -
Install the GPG key.
curl -s https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH | gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg --import && chmod 644 /usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg -
Add the repository.
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg] https://packages.wazuh.com/5.x/apt/ stable main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wazuh.list -
Update the packages information.
apt-get update
Installing the Wazuh indexer package
Yum
yum -y install wazuh-indexer
APT
apt-get -y install wazuh-indexer
Configuring the Wazuh indexer
Edit the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml configuration file and replace the following values:
a. network.host: Sets the address of this node for both HTTP and transport traffic. The node will bind to this address and use it as its publish address. Accepts an IP address or a hostname.
Use the same node address set in config.yml to create the SSL certificates.
b. node.name: Name of the Wazuh indexer node as defined in the config.yml file. For example, node-1.
c. cluster.initial_cluster_manager_nodes: List of the names of the master-eligible nodes. These names are defined in the config.yml file. Uncomment the node-2 and config.yml and node-3lines, change the names, or add more lines, according to your onfig.yml`definitions.
cluster.initial_cluster_manager_nodes:
- "node-1"
- "node-2"
- "node-3"
d. discovery.seed_hosts: List of the addresses of the master-eligible nodes. Each element can be either an IP address or a hostname. You may leave this setting commented if you are configuring the Wazuh indexer as a single node. For multi-node configurations, uncomment this setting and set the IP addresses of each master-eligible node.
discovery.seed_hosts:
- "10.0.0.1"
- "10.0.0.2"
- "10.0.0.3"
e. plugins.security.nodes_dn: List of the Distinguished Names of the certificates of all the Wazuh indexer cluster nodes. Uncomment the lines for node-2 and node-3 and change the common names (CN) and values according to your settings and your config.yml definitions.
plugins.security.nodes_dn:
- "CN=node-1,OU=Wazuh,O=Wazuh,L=California,C=US"
- "CN=node-2,OU=Wazuh,O=Wazuh,L=California,C=US"
- "CN=node-3,OU=Wazuh,O=Wazuh,L=California,C=US"
Deploying certificates
Note: Make sure that a copy of the
nazuh-certificates.tarfile, created during the initial configuration step, is placed in your working directory.
Run the following commands, replacing <INDEXER_NODE_NAME> with the name of the Wazuh indexer node you are configuring as defined in config.yml. For example, node-1. This deploys the SSL certificates to encrypt communications between the Wazuh central components.
NODE_NAME=<INDEXER_NODE_NAME>
mkdir -p /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs
tar -xf ./wazuh-certificates.tar -C /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/ ./$NODE_NAME.pem ./$NODE_NAME-key.pem ./admin.pem ./admin-key.pem ./root-ca.pem
mv -n /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/$NODE_NAME.pem /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/indexer.pem
mv -n /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/$NODE_NAME-key.pem /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/indexer-key.pem
chmod 500 /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs
chmod 400 /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/*
chown -R wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/certs
Starting the service
Enable and start the Wazuh indexer service.
Systemd
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable wazuh-indexer
systemctl start wazuh-indexer
SysV init
Choose one option according to the operating system used.
a. RPM-based operating system:
chkconfig --add wazuh-indexer
service wazuh-indexer start
b. Debian-based operating system:
update-rc.d wazuh-indexer defaults 95 10
service wazuh-indexer start
Repeat this stage of the installation process for every Wazuh indexer node in your cluster. Then proceed with initializing your single-node or multi-node cluster in the next stage.
3. Cluster initialization
Run the Wazuh indexer indexer-security-init.sh script on any Wazuh indexer node to load the new certificates information and start the single-node or multi-node cluster.
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/indexer-security-init.sh
Note: You only have to initialize the cluster once, there is no need to run this command on every node.
Testing the cluster installation
-
Replace
<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>and run the following commands to confirm that the installation is successful.curl -k -u admin:admin https://<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADRESS>:9200Output
{ "name" : "node-1", "cluster_name" : "wazuh-cluster", "cluster_uuid" : "095jEW-oRJSFKLz5wmo5PA", "version" : { "number" : "7.10.2", "build_type" : "rpm", "build_hash" : "db90a415ff2fd428b4f7b3f800a51dc229287cb4", "build_date" : "2023-06-03T06:24:25.112415503Z", "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "9.6.0", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "7.10.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "7.0.0" }, "tagline" : "The OpenSearch Project: https://opensearch.org/" } -
Replace
<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>and run the following command to check if the single-node or multi-node cluster is working correctly.curl -k -u admin:admin https://<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>:9200/_cat/nodes?v
Configuration Files
Initialization plugin settings
Timeout for the OpenSearch client
- Key:
plugins.setup.timeout - Type: Integer
- Default:
30 - Minimum:
5 - Maximum:
120 - Description: Timeout in seconds for index and search operations.
Backoff (delay) for the retry mechanism
- Key:
plugins.setup.backoff - Type: Integer
- Default:
15 - Minimum:
5 - Maximum:
60 - Description: Delay in seconds for the retry mechanism involving initialization tasks.
Example
Below, there is an example of custom values for these settings within the opensearch.yml file:
plugins.setup.timeout: 60
plugins.setup.backoff: 30
Security - Access Control
Wazuh Indexer uses the OpenSearch Security plugin to manage access control and security features.
The configuration files for the security plugin are located under the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-security/ directory by default.
Modifying these files directly is not recommened. Instead, use the Wazuh Dashboard Security plugin to create new security resouces. See Define Users and Roles.
Among these files, Wazuh Indexer uses these particularly to add its own security resources:
-
internal_users.yml: Defines the internal users for the Wazuh Indexer. Each user has a hashed password, reserved status, backend roles, and a description. -
roles.yml: Defines the roles and their permissions within the Wazuh Indexer. Each role specifies the cluster permissions, index permissions, and tenant permissions. -
roles_mapping.yml: Maps users and backend roles to the defined roles. This file specifies which users or backend roles have access to each role.
The Access Control section contains information about the security resources added to the Wazuh Indexer by default.
Wazuh Indexer Initialization plugin
The wazuh-indexer-setup plugin is a module composing the Wazuh Indexer responsible for the initialization of the indices required by Wazuh to store all the data gathered and generated by other Central Components, such as the agents and the server (engine).
The Wazuh Indexer Setup Plugin in responsible for:
- Create the index templates, to define the mappings and settings for the indices.
- Create the initial indices. We distinguish between stateful and stream indices. While stream indices contain immutable time-series data and are rolled over periodically, stateful indices store dynamic data that can change over time and reside in a single index.
- Stream indices are created with a data stream configuration and an ISM rollover policy.
Indices
The following table lists the indices created by this plugin.
Stream indices
| Index | Description |
|---|---|
wazuh‑alerts-v5 | Stores alerts generated by the Wazuh Server. These are created each time an event trips a rule with a high enough severity (this threshold is configurable). |
wazuh‑archives-v5 | Stores all events (archive data) received by the Wazuh Server, whether they trip a rule. |
wazuh‑events-v5-<category> | Stores events received by the Wazuh Server, categorized by their origin or type. Refer to Wazuh Common Schema for more information. |
Stateful indices
| Index | Description |
|---|---|
wazuh‑states-sca | Security Configuration Assessment (SCA) scan results. |
wazuh-states-fim-files | File Integrity Monitoring: information about monitored files. |
wazuh-states-fim-registry-keys | File Integrity Monitoring: information about the Windows registry (keys). |
wazuh-states-fim-registry-values | File Integrity Monitoring: information about the Windows registry (values). |
wazuh-states-inventory-browser-extensions | Stores browser extensions/add-ons detected on the endpoint (Chromium-based browsers — Chrome/Edge/Brave/Opera —, Firefox, and Safari). |
wazuh-states-inventory-groups | Stores existing groups on the endpoint. |
wazuh-states-inventory-hardware | Basic information about the hardware components of the endpoint. |
wazuh-states-inventory-hotfixes | Contains information about the updates installed on Windows endpoints. This information is used by the vulnerability detector module to discover what vulnerabilities have been patched on Windows endpoints. |
wazuh-states-inventory-interfaces | Stores information (up and down interfaces) as well as packet transfer information about the interfaces on a monitored endpoint. |
wazuh-states-inventory-monitoring | Stores the connection status history of Wazuh agents (active, disconnected, pending, or never connected). The index is used by the Wazuh Dashboard to display agent status and historical trends. |
wazuh-states-inventory-networks | Stores the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses associated with each network interface, as referenced in the wazuh-states-inventory-interfaces index. |
wazuh-states-inventory-packages | Stores information about the currently installed software on the endpoint. |
wazuh-states-inventory-ports | Basic information about open network ports on the endpoint. |
wazuh-states-inventory-processes | Stores the detected running processes on the endpoints. |
wazuh-states-inventory-protocols | Stores routing configuration details for each network interface, as referenced in the wazuh-states-inventory-interfaces index. |
wazuh-states-inventory-services | Stores system services detected on the endpoint (Windows Services, Linux systemd units, and macOS launchd daemons/agents). |
wazuh-states-inventory-system | Operating system information, hostname and architecture. |
wazuh-states-inventory-users | Stores existing users on the endpoint. |
wazuh-states-vulnerabilities | Active vulnerabilities on the endpoint and its details. |
wazuh-statistics | Stores statistics about the Wazuh Server usage and performance. The information includes the number of events decoded, bytes received, and TCP sessions. |
Install
The wazuh-indexer-setup plugin is part of the official Wazuh Indexer packages and is installed by default. However, to manually install the plugin, follow the next steps.
Note: You need to use the
wazuh-indexerorrootuser to run these commands.
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/opensearch-plugin install file://[absolute-path-to-the-plugin-zip]
Once installed, restart the Wazuh Indexer service.
Uninstall
Note You need to use the
wazuh-indexerorrootuser to run these commands.
To list the installed plugins, run:
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/opensearch-plugin list
To remove a plugin, use its name as a parameter with the remove command:
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/opensearch-plugin remove <plugin-name>
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/bin/opensearch-plugin remove wazuh-indexer-setup
Architecture
Design
The plugin implements the ClusterPlugin interface in order to be able to hook into the node’s lifecycle overriding the onNodeStarted() method.
The SetupPlugin class holds the list of indices to create. The logic for the creation of the index templates and the indices is encapsulated in the Index abstract class. Each subclass can override this logic if necessary. The SetupPlugin::onNodeStarted() method invokes the Index::initialize() method, effectively creating every index in the list.
By design, the plugin will overwrite any existing index template under the same name.
Retry mechanism
The plugin features a retry mechanism to handle transient faults. In case of a temporal failure (timeouts or similar) during the initialization of the indices, the task is retried after a given amount of time (backoff). If two consecutive faults occur during the initialization of the same index, the initialization process is halted, and the node is shut down. Proper logging is in place to notify administrators before the shutdown occurs.
The backoff time is configurable. Head to Configuration Files for more information.
Replica configuration
During the node initialization, the plugin checks for the presence of the cluster.default_number_of_replicas setting in the node configuration. If this setting is defined, the plugin automatically updates the cluster’s persistent settings with this value. This ensures that the default number of replicas is consistently applied across the cluster as defined in the configuration file.
Class diagram
---
title: Wazuh Indexer setup plugin
---
classDiagram
%% Classes
class IndexInitializer
<<interface>> IndexInitializer
class Index
<<abstract>> Index
class IndexStateManagement
class WazuhIndex
<<abstract>> WazuhIndex
class StateIndex
class StreamIndex
%% Relations
IndexInitializer <|-- Index : implements
Index <|-- IndexStateManagement
Index <|-- WazuhIndex
WazuhIndex <|-- StateIndex
WazuhIndex <|-- StreamIndex
%% Schemas
class IndexInitializer {
+createIndex(String index) void
+createTemplate(String template) void
}
class Index {
Client client
ClusterService clusterService
IndexUtils utils
String index
String template
+Index(String index, String template)
+setClient(Client client) IndexInitializer
+setClusterService(ClusterService clusterService) IndexInitializer
+setIndexUtils(IndexUtils utils) IndexInitializer
+indexExists(String indexName) bool
+initialize() void
+createIndex(String index) void
+createTemplate(String template) void
%% initialize() podría reemplazarse por createIndex() y createTemplate()
}
class IndexStateManagement {
-List~String~ policies
+initialize() void
-createPolicies() void
-indexPolicy(String policy) void
}
class WazuhIndex {
}
class StreamIndex {
-String alias
+StreamIndex(String index, String template, String alias)
+createIndex(String index)
}
class StateIndex {
}
Sequence diagram
Note Calls to
Clientare asynchronous.
sequenceDiagram
actor Node
participant SetupPlugin
participant Index
participant Client
Node->>SetupPlugin: plugin.onNodeStarted()
activate SetupPlugin
Note over Node,SetupPlugin: Invoked on Node::start()
activate Index
loop i..n indices
SetupPlugin->>Index: i.initialize()
Index-)Client: createTemplate(i)
Client--)Index: response
Index-)Client: indexExists(i)
Client--)Index: response
alt index i does not exist
Index-)Client: createIndex(i)
Client--)Index: response
end
end
deactivate Index
deactivate SetupPlugin
Wazuh Common Schema
Refer to the docs for complete definitions of the indices. The indices inherit the settings and mappings defined in the index templates.
JavaDoc
The plugin is documented using JavaDoc. You can compile the documentation using the Gradle task for that purpose. The generated JavaDoc is in the build/docs folder.
./gradlew javadoc
Wazuh Common Schema
The Wazuh Common Schema (WCS) is a standardized structure for organizing and categorizing security event data collected by Wazuh. It is designed to facilitate data analysis, correlation, and reporting across different data sources and types.
Categorization
The Wazuh Common Schema categorizes events into several key areas to streamline data management and analysis.
The index mappings and settings for subcategories take precedence over those from the main category. In OpenSearch, index templates are applied in order of their “priority” value: templates with a lower priority are applied first, and those with a higher priority are applied afterward, allowing them to override previous settings. This means the index template for the main category is applied first (priority=1), and then the subcategory template (priority=10) is applied on top of it, so subcategory-specific settings override the main category defaults.
Access Management
None yet.
Applications and Web Servers
| Integration Name | Subcategory | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Apache integration | Apache | Applications |
| NGINX integration | - | Applications |
| IIS integration | - | Applications |
| Apache Tomcat integration | Apache | Applications |
| WebSphere Application Server integration | - | Applications |
| Oracle WebLogic Server integration | - | Applications |
| Spring Boot integration | - | Applications |
| squid | - | Applications |
Cloud Services
| Integration Name | Subcategory | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Security Lake | AWS | Cloud Services |
| AWS | AWS | Cloud Services |
| AWS Bedrock | AWS | Cloud Services |
| AWS Logs | AWS | Cloud Services |
| AWS Fargate | AWS | Cloud Services |
| AWS Firehose | AWS | Cloud Services |
| Azure | Azure | Cloud Services |
| Azure Blob Storage | Azure | Cloud Services |
| Azure App Service | Azure | Cloud Services |
| Azure Functions | Azure | Cloud Services |
| Azure Metrics | Azure | Cloud Services |
| Azure OpenAI | Azure | Cloud Services |
| Cisco Umbrella | - | Cloud Services |
| GCP | GCP | Cloud Services |
| Google SCC | GCP | Cloud Services |
Network Activity
| Integration Name | Subcategory | Category |
|---|---|---|
| iptables | - | Network Activity |
| Cisco ASA | Cisco | Network Activity |
| Cisco IOS | Cisco | Network Activity |
| Cisco Meraki | Cisco | Network Activity |
| Cisco Aironet | Cisco | Network Activity |
| Fortinet Fortigate | Fortinet | Network Activity |
| CheckPoint | - | Network Activity |
| SonicWall | - | Network Activity |
| F5 BIG-IP | - | Network Activity |
| pfSense | - | Network Activity |
| Fortinet Fortiproxy | Fortinet | Network Activity |
Security
| Integration Name | Subcategory | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Snort | - | Security |
| Suricata | - | Security |
| ModSecurity | - | Security |
| Zeek | - | Security |
System Activity
| Integration Name | Subcategory | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Auditd | Linux | System Activity |
| Sysmon Linux | Linux | System Activity |
| Windows | Windows | System Activity |
| Windows DHCP | Windows | System Activity |
| Windows DNS server | Windows | System Activity |
| Windows Exchange server | Windows | System Activity |
| ULS | macOS | System Activity |
Other
None yet.
Indices
wazuh-events-v5-access-management-000001
wazuh-events-v5-applications-000001
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services-000001
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services-aws-000001
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services-azure-000001
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services-gcp-000001
wazuh-events-v5-network-activity-000001
wazuh-events-v5-other-000001
wazuh-events-v5-security-000001
wazuh-events-v5-system-activity-000001
Aliases
wazuh-events-v5-access-management
wazuh-events-v5-applications
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services-aws
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services-azure
wazuh-events-v5-cloud-services-gcp
wazuh-events-v5-network-activity
wazuh-events-v5-other
wazuh-events-v5-security
wazuh-events-v5-system-activity
Content Manager
The Content Manager is a Wazuh Indexer plugin responsible for managing detection content — rules, decoders, integrations, key-value databases (KVDBs), and Indicators of Compromise (IoCs). It synchronizes content from the Wazuh Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) API, provides a REST API for user-generated content, and communicates with the Wazuh Engine to activate changes.
CTI Synchronization
The Content Manager periodically synchronizes content from the Wazuh CTI API. Two content contexts are managed:
- Catalog context (
development_0.0.3): Contains detection rules, decoders, integrations, KVDBs, and the routing policy. - IoC context (
ioc_provider): Contains Indicators of Compromise for threat detection.
Each context has an associated consumer that tracks synchronization state (current offset, snapshot URL) in the .cti-consumers index.
Snapshot Initialization
On first run (when the local offset is 0), the Content Manager performs a full snapshot initialization:
- Fetches the latest snapshot URL from the CTI API.
- Downloads and extracts the ZIP archive.
- Indexes the content into the appropriate system indices using bulk operations.
- Records the snapshot offset in
.cti-consumers.
Incremental Updates
When the local offset is behind the remote offset, the Content Manager fetches changes in batches (up to 1000 per request) and applies create, update, and delete operations to the content indices. The local offset is updated after each successful batch.
Sync Schedule
By default, synchronization runs:
- On plugin startup (
plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_start: true) - Periodically every 60 minutes (
plugins.content_manager.catalog.sync_interval: 60)
The periodic job is registered with the OpenSearch Job Scheduler and tracked in the .wazuh-content-manager-jobs index.
User-Generated Content
The Content Manager provides a full CUD REST API for creating custom detection content:
- Rules: Custom detection rules associated with an integration.
- Decoders: Custom log decoders associated with an integration.
- Integrations: Logical groupings of related rules, decoders, and KVDBs.
- KVDBs: Key-value databases used by rules and decoders for lookups.
User-generated content is stored in the draft space and is separate from the CTI-managed standard space. This separation ensures that user customizations never conflict with upstream CTI content.
See the API Reference for endpoint details.
Content Spaces
The Content Manager organizes content into spaces:
| Space | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard | Read-only content synced from the CTI API. This is the baseline detection content. |
| Draft | Writable space for user-generated content. CUD operations target this space. |
| Test | Used for logtest operations and content validation before final promotion. |
| Custom | The final space for user content. Content promoted to this space is used by the Wazuh Engine (via the manager package) to actively decode and process logs. |
Content flows through spaces in a promotion chain: Draft → Test → Custom. The Standard space exists independently as the upstream CTI baseline. Each space maintains its own copies of rules, decoders, integrations, KVDBs, filters, and the routing policy within the system indices.
Policy Management
The routing policy defines how the Wazuh Engine processes incoming events — which integrations are active and in what order. The Content Manager provides an API to update the draft policy:
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X PUT \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/policy" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"resource": { ... }}'
Policy changes are applied to the draft space and take effect after promotion.
Promotion Workflow
The promotion workflow moves content through the space chain (Draft → Test → Custom):
- Preview changes:
GET /_plugins/_content_manager/promote?space=draftreturns a diff of what will change (additions, updates, deletions for each content type). - Execute promotion:
POST /_plugins/_content_manager/promotepromotes the content from the source space to the next space in the chain.
The promotion chain works as follows:
- Draft → Test: Content is promoted for validation and logtest operations.
- Test → Custom: Once validated, content is promoted to the Custom space where it becomes active — the Wazuh Engine (via the manager package) uses this space to decode and process logs in production.
During promotion, the Content Manager:
- Sends updated content to the Engine
- Validates the configuration
- Triggers a configuration reload
- Updates the target space to reflect the promoted content
Engine Communication
The Content Manager communicates with the Wazuh Engine through a Unix domain socket located at:
/usr/share/wazuh-indexer/engine/sockets/engine-api.sock
This socket is used for:
- Logtest: Sends a log event to the Engine for analysis and returns the decoded/matched result.
- Content validation: Validates rules and decoders before promotion.
- Configuration reload: Signals the Engine to reload its configuration after promotion.
System Indices
The Content Manager uses the following system indices:
| Index | Description |
|---|---|
.cti-consumers | Synchronization state for each CTI context/consumer pair (offsets, snapshot URLs) |
.cti-rules | Detection rules (both CTI-synced and user-generated, across all spaces) |
.cti-decoders | Log decoders |
.cti-integrations | Integration definitions |
.cti-kvdbs | Key-value databases |
.cti-policies | Routing policies |
.cti-iocs | Indicators of Compromise |
.engine-filters | Engine filters (routing filters for event classification) |
.wazuh-content-manager-jobs | Job Scheduler metadata for the periodic sync job |
CTI Subscription
To synchronize content from the CTI API, the Wazuh Indexer requires a valid subscription token. The subscription is managed through the REST API:
- Register a subscription with a device code obtained from the Wazuh CTI Console.
- The Content Manager stores the token and uses it for all CTI API requests.
- Without a valid subscription, sync operations return a
Token not founderror.
See Subscription Management in the API Reference.
Architecture
The Content Manager plugin operates within the Wazuh Indexer environment. It is composed of several components that handle REST API requests, background job scheduling, content synchronization, user-generated content management, and Engine communication.
Components
REST Layer
Exposes HTTP endpoints under /_plugins/_content_manager/ for:
- Subscription management (register, get, delete CTI tokens)
- Manual content sync trigger
- CUD operations on rules, decoders, integrations, and KVDBs
- Policy management
- Promotion preview and execution
- Logtest execution
- Content validation and promotion
CTI Console
Manages authentication with the Wazuh CTI API. Stores subscription tokens used for all CTI requests. Without a valid token, sync operations are rejected.
Job Scheduler (CatalogSyncJob)
Implements the OpenSearch JobSchedulerExtension interface. Registers a periodic job (wazuh-catalog-sync-job) that triggers content synchronization at a configurable interval (default: 60 minutes). The job metadata is stored in .wazuh-content-manager-jobs.
Consumer Service
Orchestrates synchronization for each context/consumer pair. Compares local offsets (from .cti-consumers) with remote offsets from the CTI API, then delegates to either the Snapshot Service or Update Service.
Snapshot Service
Handles initial content loading. Downloads a ZIP snapshot from the CTI API, extracts it, and bulk-indexes content into the appropriate system indices. Performs data enrichment (e.g., converting JSON payloads to YAML for decoders).
Update Service
Handles incremental updates. Fetches change batches from the CTI API based on offset differences and applies create, update, and delete operations to content indices.
Security Analytics Service
Interfaces with the OpenSearch Security Analytics plugin. Creates, updates, and deletes Security Analytics rules, integrations, and detectors to keep them in sync with CTI content.
Space Service
Manages the four content spaces (standard, draft, test, custom). Routes CUD operations to the correct space partitions within system indices. Handles promotion by computing diffs between spaces in the promotion chain (Draft → Test → Custom).
Engine Client
Communicates with the Wazuh Engine via Unix domain socket at /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/engine/sockets/engine-api.sock. Used for logtest execution, content validation, and configuration reload.
Data Flows
CTI Sync (Snapshot)
Job Scheduler triggers
→ Consumer Service checks .cti-consumers (offset = 0)
→ Snapshot Service downloads ZIP from CTI API
→ Extracts and bulk-indexes into .cti-rules, .cti-decoders, etc.
→ Updates .cti-consumers with new offset
→ Security Analytics Service creates detectors
CTI Sync (Incremental)
Job Scheduler triggers
→ Consumer Service checks .cti-consumers (local_offset < remote_offset)
→ Update Service fetches change batches from CTI API
→ Applies CREATE/UPDATE/DELETE to content indices
→ Updates .cti-consumers offset
→ Security Analytics Service syncs changes
User-Generated Content (CUD)
REST request (POST/PUT/DELETE)
→ Space Service routes to draft space
→ Writes to .cti-rules / .cti-decoders / .cti-integrations / .cti-kvdbs
→ Returns created/updated/deleted resource
Promotion
GET /promote?space=draft
→ Space Service computes diff (draft vs standard)
→ Returns changes preview (adds, updates, deletes per content type)
POST /promote
→ Space Service sends draft content to Engine via Unix socket
→ Engine validates configuration
→ Engine reloads configuration
→ Standard space updated to match promoted content
Index Structure
Each content index (e.g., .cti-rules) stores documents from all three spaces. Documents are differentiated by internal metadata fields that indicate their space membership. The document _id is a UUID assigned at creation time.
Example document structure in .cti-rules:
{
"_index": ".cti-rules",
"_id": "a1b2c3d4-e5f6-7890-abcd-ef1234567890",
"_source": {
"title": "SSH brute force attempt",
"integration": "openssh",
"space.name": "draft",
...
}
}
The .cti-consumers index stores one document per context/consumer pair:
{
"_index": ".cti-consumers",
"_id": "development_0.0.3_development_0.0.3_test",
"_source": {
"name": "development_0.0.3_test",
"context": "development_0.0.3",
"local_offset": 3932,
"remote_offset": 3932,
"snapshot_link": "https://cti-pre.wazuh.com/store/contexts/development_0.0.3/consumers/development_0.0.3_test/3932_1770988130.zip"
}
}
Configuration
The Content Manager plugin is configured through settings in opensearch.yml. All settings use the plugins.content_manager prefix.
Settings Reference
| Setting | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
plugins.content_manager.cti.api | String | https://cti-pre.wazuh.com/api/v1 | Base URL for the Wazuh CTI API |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.sync_interval | Integer | 60 | Sync interval in minutes. Valid range: 1–1440 |
plugins.content_manager.max_items_per_bulk | Integer | 25 | Maximum documents per bulk indexing request. Valid range: 10–25 |
plugins.content_manager.max_concurrent_bulks | Integer | 5 | Maximum concurrent bulk operations. Valid range: 1–5 |
plugins.content_manager.client.timeout | Long | 10 | HTTP client timeout in seconds for CTI API requests. Valid range: 10–50 |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_start | Boolean | true | Trigger content sync when the plugin starts |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_schedule | Boolean | true | Enable the periodic sync job |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.content.context | String | development_0.0.3 | CTI catalog content context identifier |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.content.consumer | String | development_0.0.3_test | CTI catalog content consumer identifier |
plugins.content_manager.ioc.content.context | String | ioc_provider | IoC content context identifier |
plugins.content_manager.ioc.content.consumer | String | iocp_v1 | IoC content consumer identifier |
plugins.content_manager.catalog.create_detectors | Boolean | true | Automatically create Security Analytics detectors from CTI content |
Configuration Examples
Default Configuration
No configuration is required for default behavior. The Content Manager will sync content every 60 minutes using the pre-configured CTI contexts.
Custom Sync Interval
To sync content every 30 minutes:
# opensearch.yml
plugins.content_manager.catalog.sync_interval: 30
Disable Automatic Sync
To disable all automatic synchronization and only sync manually via the API:
# opensearch.yml
plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_start: false
plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_schedule: false
Content can still be synced on demand using:
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/update"
Custom CTI API Endpoint
To point to a different CTI API (e.g., production):
# opensearch.yml
plugins.content_manager.cti.api: "https://cti.wazuh.com/api/v1"
Tune Bulk Operations
For environments with limited resources, reduce the bulk operation concurrency:
# opensearch.yml
plugins.content_manager.max_items_per_bulk: 10
plugins.content_manager.max_concurrent_bulks: 2
plugins.content_manager.client.timeout: 30
Disable Security Analytics Detector Creation
If you do not use the OpenSearch Security Analytics plugin:
# opensearch.yml
plugins.content_manager.catalog.create_detectors: false
Notes
- Changes to
opensearch.ymlrequire a restart of the Wazuh Indexer to take effect. - The
contextandconsumersettings should only be changed if instructed by Wazuh support or documentation, as they must match valid CTI API contexts. - The sync interval is enforced by the OpenSearch Job Scheduler. The actual sync timing may vary slightly depending on cluster load.
API Reference
The Content Manager plugin exposes a REST API under /_plugins/_content_manager/. All endpoints require authentication.
Subscription Management
Get CTI Subscription
Retrieves the current CTI subscription token.
Request
- Method:
GET - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription"
Example Response (subscription exists)
{
"access_token": "AYjcyMzY3ZDhiNmJkNTY",
"token_type": "Bearer"
}
Example Response (no subscription)
{
"message": "Token not found",
"status": 404
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Subscription token returned |
| 404 | No subscription registered |
Register CTI Subscription
Registers a new CTI subscription using a device code obtained from the Wazuh CTI Console.
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
device_code | String | Yes | Device authorization code from CTI Console |
client_id | String | Yes | OAuth client identifier |
expires_in | Integer | Yes | Token expiration time in seconds |
interval | Integer | Yes | Polling interval in seconds |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"device_code": "GmRhmhcxhwAzkoEqiMEg_DnyEysNkuNhszIySk9eS",
"client_id": "a17c21ed",
"expires_in": 1800,
"interval": 5
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "Subscription created successfully",
"status": 201
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 201 | Subscription registered successfully |
| 400 | Missing required fields (device_code, client_id, expires_in, interval) |
| 401 | Unauthorized — endpoint accessed by unexpected user |
| 500 | Internal error |
Delete CTI Subscription
Removes the current CTI subscription token and revokes all associated credentials.
Request
- Method:
DELETE - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X DELETE \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription"
Example Response (success)
{
"message": "Subscription deleted successfully",
"status": 200
}
Example Response (no subscription)
{
"message": "Token not found",
"status": 404
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Subscription deleted |
| 404 | No subscription to delete |
Content Updates
Trigger Manual Sync
Triggers an immediate content synchronization with the CTI API. Requires a valid subscription.
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/update
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/update"
Example Response (success)
{
"message": "Content update triggered successfully",
"status": 200
}
Example Response (no subscription)
{
"message": "Token not found. Please create a subscription before attempting to update.",
"status": 404
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Sync triggered successfully |
| 404 | No subscription token found |
| 409 | A content update is already in progress |
| 429 | Rate limit exceeded |
| 500 | Internal error during sync |
Logtest
Execute Logtest
Sends a log event to the Wazuh Engine for analysis and returns the decoded and matched result. The Indexer acts as a pass-through: it forwards the payload to the Engine via Unix socket and returns the Engine’s response.
Note: A testing policy must be loaded in the Engine for logtest to execute successfully. Load a policy via the policy promotion endpoint.
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/logtest
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
queue | Integer | Yes | Queue number for logtest execution |
location | String | Yes | Log file path or logical source location |
event | String | Yes | Raw log event to test |
agent_metadata | Object | No | Optional agent metadata passed to the Engine |
trace_level | String | No | Trace verbosity: NONE, BASIC, or FULL |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/logtest" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"queue": 1,
"location": "/var/log/auth.log",
"agent_metadata": {},
"event": "Dec 19 12:00:00 host sshd[123]: Failed password for root from 10.0.0.1 port 12345 ssh2",
"trace_level": "NONE"
}'
Example Response (success)
{
"status": "OK",
"result": {
"output": "{\"wazuh\":{\"protocol\":{\"queue\":1,\"location\":\"syscheck\"},\"integration\":{\"category\":\"Security\",\"name\":\"integration/wazuh-core/0\",\"decoders\":[\"core-wazuh-message\",\"integrations\"]}},\"event\":{\"original\":\"Dec 19 12:00:00 host sshd[123]: Failed password for root from 10.0.0.1 port 12345 ssh2\"},\"@timestamp\":\"2026-02-19T12:00:00Z\"}",
"asset_traces": [
{
"asset": "decoder/core-wazuh-message/0",
"success": true,
"traces": ["@timestamp: get_date -> Success"]
}
]
}
}
Example Response (Engine unavailable)
{
"message": "Error communicating with Engine socket: Connection refused",
"status": 500
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Logtest executed successfully |
| 400 | Invalid request body |
| 500 | Engine socket communication error |
Policy
Update Draft Policy
Updates the routing policy in the draft space. The policy defines which integrations are active, the root decoder, enrichment types, and how events are routed through the Engine.
Note: The
integrationsarray allows reordering but does not allow adding or removing entries — integration membership is managed via the integration CRUD endpoints.
Request
- Method:
PUT - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/policy
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
resource | Object | Yes | The policy resource object |
Fields within resource:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | String | No | Human-readable policy name |
root_decoder | String | No | Identifier of the root decoder for event processing |
integrations | Array | No | List of integration IDs (reorder only, no add/remove) |
filters | Array | No | List of filter UUIDs |
enrichments | Array | No | Enrichment types: file, domain-name, ip, url, geo (no duplicates) |
author | String | Yes | Author of the policy |
description | String | Yes | Brief description |
documentation | String | Yes | Documentation text or URL |
references | Array | Yes | External reference URLs |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X PUT \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/policy" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"resource": {
"title": "Draft policy",
"root_decoder": "",
"integrations": [
"f16f33ec-a5ea-4dc4-bf33-616b1562323a"
],
"filters": [],
"enrichments": [],
"author": "Wazuh Inc.",
"description": "Custom policy",
"documentation": "",
"references": [
"https://wazuh.com"
]
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "kQPmV5wBi_TgruUn97RT",
"status": 200
}
The message field contains the OpenSearch document ID of the updated policy.
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Policy updated |
| 400 | Missing resource field, missing required fields, or invalid enrichments |
| 500 | Internal error |
Rules
Create Rule
Creates a new detection rule in the draft space. The rule is linked to the specified parent integration and validated by the Security Analytics Plugin.
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/rules
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
integration | String | Yes | UUID of the parent integration (must be in draft space) |
resource | Object | Yes | The rule definition |
Fields within resource:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | String | Yes | Rule title (must be unique within the draft space) |
description | String | No | Rule description |
author | String | No | Rule author |
sigma_id | String | No | Sigma rule ID |
references | Array | No | Reference URLs |
enabled | Boolean | No | Whether the rule is enabled |
status | String | No | Rule status (e.g., experimental, stable) |
level | String | No | Alert level (e.g., low, medium, high, critical) |
logsource | Object | No | Log source definition (product, category) |
detection | Object | No | Sigma detection logic with condition and selection fields |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/rules" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"integration": "6b7b7645-00da-44d0-a74b-cffa7911e89c",
"resource": {
"title": "Test Rule",
"description": "A Test rule",
"author": "Tester",
"sigma_id": "string",
"references": [
"https://wazuh.com"
],
"enabled": true,
"status": "experimental",
"logsource": {
"product": "system",
"category": "system"
},
"detection": {
"condition": "selection",
"selection": {
"event.action": [
"hash_test_event"
]
}
},
"level": "low"
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "6e1c43f1-f09b-4cec-bb59-00e3a52b7930",
"status": 201
}
The message field contains the UUID of the created rule.
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 201 | Rule created |
| 400 | Missing fields, duplicate title, integration not in draft space, or validation failure |
| 500 | Internal error or SAP unavailable |
Update Rule
Updates an existing rule in the draft space.
Request
- Method:
PUT - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/rules/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String (UUID) | Yes | Rule document ID |
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
resource | Object | Yes | Updated rule definition (same fields as create) |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X PUT \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/rules/6e1c43f1-f09b-4cec-bb59-00e3a52b7930" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"resource": {
"title": "Test Hash Generation Rule",
"description": "A rule to verify that SHA-256 hashes are calculated correctly upon creation.",
"author": "Tester",
"status": "experimental",
"logsource": {
"product": "system",
"category": "system"
},
"detection": {
"condition": "selection",
"selection": {
"event.action": [
"hash_test_event"
]
}
},
"level": "low"
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "6e1c43f1-f09b-4cec-bb59-00e3a52b7930",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Rule updated |
| 400 | Invalid request, not in draft space, or validation failure |
| 404 | Rule not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
Delete Rule
Deletes a rule from the draft space. The rule is also removed from any integrations that reference it.
Request
- Method:
DELETE - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/rules/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String (UUID) | Yes | Rule document ID |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X DELETE \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/rules/6e1c43f1-f09b-4cec-bb59-00e3a52b7930"
Example Response
{
"message": "6e1c43f1-f09b-4cec-bb59-00e3a52b7930",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Rule deleted |
| 404 | Rule not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
Decoders
Create Decoder
Creates a new log decoder in the draft space. The decoder is validated against the Wazuh Engine before being stored, and automatically linked to the specified integration.
Note: A testing policy must be loaded in the Engine for decoder validation to succeed.
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/decoders
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
integration | String | Yes | UUID of the parent integration (must be in draft space) |
resource | Object | Yes | The decoder definition |
Fields within resource:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | String | Decoder name identifier (e.g., decoder/core-wazuh-message/0) |
enabled | Boolean | Whether the decoder is enabled |
check | Array | Decoder check logic — array of condition objects |
normalize | Array | Normalization rules — array of mapping objects |
metadata | Object | Decoder metadata (see below) |
Fields within metadata:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
title | String | Human-readable decoder title |
description | String | Decoder description |
module | String | Module name |
compatibility | String | Compatibility description |
author | Object | Author info (name, email, url) |
references | Array | Reference URLs |
versions | Array | Supported versions |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/decoders" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"integration": "0aa4fc6f-1cfd-4a7c-b30b-643f32950f1f",
"resource": {
"enabled": true,
"metadata": {
"author": {
"name": "Wazuh, Inc."
},
"compatibility": "All wazuh events.",
"description": "Base decoder to process Wazuh message format.",
"module": "wazuh",
"references": [
"https://documentation.wazuh.com/"
],
"title": "Wazuh message decoder",
"versions": [
"Wazuh 5.*"
]
},
"name": "decoder/core-wazuh-message/0",
"check": [
{
"tmp_json.event.action": "string_equal(\"netflow_flow\")"
}
],
"normalize": [
{
"map": [
{
"@timestamp": "get_date()"
}
]
}
]
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "d_0a6aaebe-dd0b-44cc-a787-ffefd4aac175",
"status": 201
}
The message field contains the UUID of the created decoder (prefixed with d_).
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 201 | Decoder created |
| 400 | Missing integration field, integration not in draft space, or Engine validation failure |
| 500 | Engine unavailable or internal error |
Update Decoder
Updates an existing decoder in the draft space. The decoder is re-validated against the Wazuh Engine.
Request
- Method:
PUT - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/decoders/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String | Yes | Decoder document ID |
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
resource | Object | Yes | Updated decoder definition (same fields as create) |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X PUT \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/decoders/bb6d0245-8c1d-42d1-8edb-4e0907cf45e0" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"resource": {
"name": "decoder/test-decoder/0",
"enabled": false,
"metadata": {
"title": "Test Decoder UPDATED",
"description": "Updated description",
"author": {
"name": "Hello there"
}
},
"check": [],
"normalize": []
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "bb6d0245-8c1d-42d1-8edb-4e0907cf45e0",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Decoder updated |
| 400 | Invalid request, not in draft space, or Engine validation failure |
| 404 | Decoder not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
Delete Decoder
Deletes a decoder from the draft space. The decoder is also removed from any integrations that reference it.
Request
- Method:
DELETE - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/decoders/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String | Yes | Decoder document ID |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X DELETE \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/decoders/acbdba85-09c4-45a0-a487-61c8eeec58e6"
Example Response
{
"message": "acbdba85-09c4-45a0-a487-61c8eeec58e6",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Decoder deleted |
| 404 | Decoder not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
Integrations
Create Integration
Creates a new integration in the draft space. An integration is a logical grouping of related rules, decoders, and KVDBs. The integration is validated against the Engine and registered in the Security Analytics Plugin.
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/integrations
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
resource | Object | Yes | The integration definition |
Fields within resource:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | String | Yes | Integration title (must be unique in draft space) |
author | String | Yes | Author of the integration |
category | String | Yes | Category (e.g., cloud-services, network-activity, security, system-activity) |
description | String | No | Description |
documentation | String | No | Documentation text or URL |
references | Array | No | Reference URLs |
enabled | Boolean | No | Whether the integration is enabled |
Note: Do not include the
idfield — it is auto-generated by the Indexer.
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/integrations" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"resource": {
"title": "azure-functions",
"author": "Wazuh Inc.",
"category": "cloud-services",
"description": "This integration supports Azure Functions app logs.",
"documentation": "https://docs.wazuh.com/integrations/azure-functions",
"references": [
"https://wazuh.com"
],
"enabled": true
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "94e5a2af-505e-4164-ab62-576a71873308",
"status": 201
}
The message field contains the UUID of the created integration.
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 201 | Integration created |
| 400 | Missing required fields (title, author, category), duplicate title, or validation failure |
| 500 | Internal error or SAP/Engine unavailable |
Update Integration
Updates an existing integration in the draft space. Only integrations in the draft space can be updated.
Request
- Method:
PUT - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/integrations/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String (UUID) | Yes | Integration document ID |
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
resource | Object | Yes | Updated integration definition |
Fields within resource (all required for update):
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | String | Yes | Integration title |
author | String | Yes | Author |
category | String | Yes | Category |
description | String | Yes | Description |
documentation | String | Yes | Documentation text or URL |
references | Array | Yes | Reference URLs |
enabled | Boolean | No | Whether the integration is enabled |
rules | Array | Yes | Ordered list of rule IDs |
decoders | Array | Yes | Ordered list of decoder IDs |
kvdbs | Array | Yes | Ordered list of KVDB IDs |
Note: The
rules,decoders, andkvdbsarrays are mandatory on update to allow reordering. Pass empty arrays[]if the integration has none.
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X PUT \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/integrations/94e5a2af-505e-4164-ab62-576a71873308" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"resource": {
"title": "azure-functions-update",
"author": "Wazuh Inc.",
"category": "cloud-services",
"description": "This integration supports Azure Functions app logs.",
"documentation": "updated documentation",
"references": [],
"enabled": true,
"rules": [],
"decoders": [],
"kvdbs": []
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "94e5a2af-505e-4164-ab62-576a71873308",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Integration updated |
| 400 | Invalid request, missing required fields, not in draft space, or duplicate title |
| 404 | Integration not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
Delete Integration
Deletes an integration from the draft space. The integration must have no attached decoders, rules, or KVDBs — delete those first.
Request
- Method:
DELETE - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/integrations/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String (UUID) | Yes | Integration document ID |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X DELETE \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/integrations/94e5a2af-505e-4164-ab62-576a71873308"
Example Response
{
"message": "94e5a2af-505e-4164-ab62-576a71873308",
"status": 200
}
Example Response (has dependencies)
{
"message": "Cannot delete integration because it has decoders attached",
"status": 400
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Integration deleted |
| 400 | Integration has dependent resources (decoders/rules/kvdbs) |
| 404 | Integration not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
KVDBs
Create KVDB
Creates a new key-value database in the draft space, linked to the specified integration.
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
integration | String | Yes | UUID of the parent integration (must be in draft space) |
resource | Object | Yes | The KVDB definition |
Fields within resource:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | String | Yes | KVDB title |
author | String | Yes | Author |
content | Object | Yes | Key-value data (at least one entry required) |
name | String | No | KVDB identifier name |
enabled | Boolean | No | Whether the KVDB is enabled |
description | String | No | Description |
documentation | String | No | Documentation |
references | Array | No | Reference URLs |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"integration": "f16f33ec-a5ea-4dc4-bf33-616b1562323a",
"resource": {
"title": "non_standard_timezones",
"name": "non_standard_timezones",
"enabled": true,
"author": "Wazuh Inc.",
"content": {
"non_standard_timezones": {
"AEST": "Australia/Sydney",
"CEST": "Europe/Berlin",
"CST": "America/Chicago",
"EDT": "America/New_York",
"EST": "America/New_York",
"IST": "Asia/Kolkata",
"MST": "America/Denver",
"PKT": "Asia/Karachi",
"SST": "Asia/Singapore",
"WEST": "Europe/London"
}
},
"description": "",
"documentation": "",
"references": [
"https://wazuh.com"
]
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "9d4ec6d5-8e30-4ea3-be05-957968c02dae",
"status": 201
}
The message field contains the UUID of the created KVDB.
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 201 | KVDB created |
| 400 | Missing integration or required resource fields, integration not in draft space |
| 500 | Internal error |
Update KVDB
Updates an existing KVDB in the draft space.
Request
- Method:
PUT - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String (UUID) | Yes | KVDB document ID |
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
resource | Object | Yes | Updated KVDB definition |
Fields within resource (all required for update):
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | String | Yes | KVDB title |
author | String | Yes | Author |
content | Object | Yes | Key-value data |
description | String | Yes | Description |
documentation | String | Yes | Documentation |
references | Array | Yes | Reference URLs |
name | String | No | KVDB identifier name |
enabled | Boolean | No | Whether the KVDB is enabled |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X PUT \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs/9d4ec6d5-8e30-4ea3-be05-957968c02dae" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"resource": {
"name": "test-UPDATED",
"enabled": true,
"author": "Wazuh.",
"content": {
"non_standard_timezones": {
"AEST": "Australia/Sydney",
"CEST": "Europe/Berlin",
"CST": "America/Chicago",
"EDT": "America/New_York",
"EST": "America/New_York",
"IST": "Asia/Kolkata",
"MST": "America/Denver",
"PKT": "Asia/Karachi",
"SST": "Asia/Singapore",
"WEST": "Europe/London"
}
},
"description": "UPDATE",
"documentation": "UPDATE.doc",
"references": [
"https://wazuh.com"
],
"title": "non_standard_timezones-2"
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "9d4ec6d5-8e30-4ea3-be05-957968c02dae",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | KVDB updated |
| 400 | Invalid request, missing required fields, or not in draft space |
| 404 | KVDB not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
Delete KVDB
Deletes a KVDB from the draft space. The KVDB is also removed from any integrations that reference it.
Request
- Method:
DELETE - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs/{id}
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Path | String (UUID) | Yes | KVDB document ID |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X DELETE \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/kvdbs/9d4ec6d5-8e30-4ea3-be05-957968c02dae"
Example Response
{
"message": "9d4ec6d5-8e30-4ea3-be05-957968c02dae",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | KVDB deleted |
| 404 | KVDB not found |
| 500 | Internal error |
Promotion
Preview Promotion Changes
Returns a preview of changes that would be applied when promoting from the specified space. This is a dry-run operation that does not modify any content.
Request
- Method:
GET - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/promote
Parameters
| Name | In | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
space | Query | String | Yes | Source space to preview: draft or test |
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/promote?space=draft"
Example Response
{
"changes": {
"kvdbs": [
{
"operation": "add",
"id": "4441d331-847a-43ed-acc6-4e09d8d6abb9"
}
],
"rules": [],
"decoders": [],
"filters": [],
"integrations": [
{
"operation": "add",
"id": "f16f33ec-a5ea-4dc4-bf33-616b1562323a"
}
],
"policy": [
{
"operation": "update",
"id": "f75bda3d-1926-4a8d-9c75-66382109ab04"
}
]
}
}
The response lists changes grouped by content type. Each change includes:
operation:add,update, orremoveid: Document ID of the affected resource
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Preview returned successfully |
| 400 | Invalid or missing space parameter |
| 500 | Internal error |
Execute Promotion
Promotes content from the source space to the next space in the promotion chain (Draft → Test → Custom). The request body must include the source space and the changes to apply (typically obtained from the preview endpoint).
Request
- Method:
POST - Path:
/_plugins/_content_manager/promote
Request Body
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
space | String | Yes | Source space: draft or test |
changes | Object | Yes | Changes to promote (from preview response) |
The changes object contains arrays for each content type (policy, integrations, kvdbs, decoders, rules, filters), each with operation and id fields.
Example Request
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/promote" \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"space": "draft",
"changes": {
"kvdbs": [],
"decoders": [
{
"operation": "add",
"id": "f56f3865-2827-464b-8335-30561b0f381b"
}
],
"rules": [],
"filters": [],
"integrations": [
{
"operation": "add",
"id": "0aa4fc6f-1cfd-4a7c-b30b-643f32950f1f"
}
],
"policy": [
{
"operation": "update",
"id": "baf9b03f-5872-4409-ab02-507b7f93d0c8"
}
]
}
}'
Example Response
{
"message": "Promotion completed successfully",
"status": 200
}
Status Codes
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | Promotion successful |
| 400 | Invalid request body or missing space field |
| 500 | Engine communication error or validation failure |
Troubleshooting
Common issues and diagnostic procedures for the Content Manager plugin.
Common Errors
“Error communicating with Engine socket: Connection refused”
The Wazuh Engine is not running or the Unix socket is not accessible.
Resolution:
-
Check the socket file exists:
ls -la /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/engine/sockets/engine-api.sock -
Ensure the Wazuh Indexer process has permission to access the socket file.
“Token not found”
No CTI subscription has been registered. The Content Manager cannot sync content without a valid subscription token.
Resolution:
-
Check the current subscription status:
curl -sk -u admin:admin \ "https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription" -
If the response is
{"message":"Token not found","status":404}, register a subscription using a device code from the Wazuh CTI Console:curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \ "https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/subscription" \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "device_code": "<your-device-code>", "client_id": "<your-client-id>", "expires_in": 900, "interval": 5 }'
Sync Not Running
Content is not being updated despite having a valid subscription.
Diagnosis:
-
Check consumer state and offsets:
curl -sk -u admin:admin \ "https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-consumers/_search?pretty"If
local_offsetequalsremote_offset, the content is already up to date. -
Check the sync job is registered and enabled:
curl -sk -u admin:admin \ "https://192.168.56.6:9200/.wazuh-content-manager-jobs/_search?pretty"Verify the job has
"enabled": trueand the schedule interval matches your configuration. -
Check if scheduled sync is enabled in
opensearch.yml:plugins.content_manager.catalog.update_on_schedule: true -
Trigger a manual sync to test:
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X POST \ "https://192.168.56.6:9200/_plugins/_content_manager/update"
Socket File Not Found
The Unix socket used for Engine communication does not exist.
Expected path: /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/engine/sockets/engine-api.sock
Resolution:
- Verify the Wazuh Engine is installed and running.
- Check the Engine configuration for the socket path.
- Ensure the
engine/sockets/directory exists under the Wazuh Indexer installation path.
Diagnostic Commands
Check Consumer State
View synchronization state for all content contexts:
curl -sk -u admin:admin \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-consumers/_search?pretty"
Example output:
{
"hits": {
"hits": [
{
"_id": "development_0.0.3_development_0.0.3_test",
"_source": {
"name": "development_0.0.3_test",
"context": "development_0.0.3",
"local_offset": 3932,
"remote_offset": 3932,
"snapshot_link": "https://cti-pre.wazuh.com/store/..."
}
}
]
}
}
local_offset == remote_offset: Content is up to date.local_offset < remote_offset: Content needs updating.local_offset == 0: Content has never been synced (snapshot required).
Check Sync Job
View the periodic sync job configuration:
curl -sk -u admin:admin \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/.wazuh-content-manager-jobs/_search?pretty"
Count Content Documents
Check how many rules, decoders, etc. have been indexed:
# Rules
curl -sk -u admin:admin "https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-rules/_count?pretty"
# Decoders
curl -sk -u admin:admin "https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-decoders/_count?pretty"
# Integrations
curl -sk -u admin:admin "https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-integrations/_count?pretty"
# KVDBs
curl -sk -u admin:admin "https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-kvdbs/_count?pretty"
# IoCs
curl -sk -u admin:admin "https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-iocs/_count?pretty"
Log Monitoring
Content Manager logs are part of the Wazuh Indexer logs. Use the following patterns to filter relevant entries:
# General Content Manager activity
grep -i "content.manager\|ContentManager\|CatalogSync" \
/var/log/wazuh-indexer/wazuh-indexer.log
# Sync job execution
grep -i "CatalogSyncJob\|consumer-sync" \
/var/log/wazuh-indexer/wazuh-indexer.log
# CTI API communication
grep -i "cti\|CTIClient" \
/var/log/wazuh-indexer/wazuh-indexer.log
# Engine socket communication
grep -i "engine.*socket\|EngineClient" \
/var/log/wazuh-indexer/wazuh-indexer.log
# Errors only
grep -i "ERROR.*content.manager" \
/var/log/wazuh-indexer/wazuh-indexer.log
Resetting Content
To force a full re-sync from snapshot, delete the consumer state document and restart the indexer:
# Delete consumer state (forces snapshot on next sync)
curl -sk -u admin:admin -X DELETE \
"https://192.168.56.6:9200/.cti-consumers/_doc/*"
# Restart indexer to trigger sync
systemctl restart wazuh-indexer
Warning: This will re-download and re-index all content from scratch. Use only when troubleshooting persistent sync issues.
Wazuh Indexer Reporting plugin
The wazuh-indexer-reporting plugin provides functionality for generating customizable reports based on data stored in the Wazuh Indexer. Most of this data originates from the Wazuh Manager, which collects and analyzes security events from registered agents. The plugin supports both scheduled and on‑demand report generation. Reports can be delivered via email or downloaded on demand through the Wazuh Dashboard or the API. Users can create, read, update, and delete custom reports. Access to these actions is governed by the Wazuh Indexer’s role‑based access control (RBAC) permissions. This plugin is built on top of OpenSearch’s native Reporting and Notifications plugins.
Usage
Configuring the email notifications channel
In Wazuh Dashboard, go to Notifications > Channels and click on Create channel:

- Fill in a name (e.g
Email notifications). - Select Email as Channel Type.
- Check SMTP sender as Sender Type.
- Click on Create SMTP sender.
- Fill in a name (e.g
mailpit). - Fill in an email address.
- In Host, type
mailpit(adapt this to your SMTP server Domain Name). - For port, type 1025 (adapt this to your SMTP server settings).
- Select None as Encryption method.
- Click on Create.

- Fill in a name (e.g
- Click on Create recipient group.
- Fill in a name (e.g
email-notifications-recipient-group). - On Emails, type any email.
- Click on Create.

- Fill in a name (e.g
The fields should now be filled in as follows:

- Click on Send test message to validate the configuration, a green message should pop up.
- Finally, click on Create.
More information on how to configure the email notifications channel can be found in the OpenSearch documentation.
Creating a new report
For more information on how to create reports, please refer to the OpenSearch documentation. The reporting plugin also allows you to create notifications following the behaviour on OpenSearch’s notifications plugin.
Generate and download a report
To create a new report you must have predefined the report settings. Once the report is configured, you can generate it by clicking the “Generate Report” button. This is only available on “On demand” report definitions as scheduled reports will be generated automatically. The report will be processed and made available for download at the Reports section on Explore -> Report.
You can also create a csv or xlsx report without a report definition by saving a search on Explore -> Discover. Remember to have an available index pattern.
Generate a report definition
Before creating a report definition you must have generated and saved a Dashboard, a Visualization, a search or a Notebook. Then you can do so at the Explore -> Reporting section, choosing the intended configuration. This generates PDF/PNG reports or CSV/XLSX reports in case a saved search is selected.
Managing permissions on reporting via RBAC
The Reporting plugin uses the Wazuh Indexer RBAC (role-based access control) system to manage permissions. This means that users must have the appropriate roles assigned to them in order to create, read, update, or delete reports. The roles can be managed through the Wazuh Dashboard Index Management -> Security -> Roles section. The following permissions are available for the Reporting plugin:
1. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/definition/create
2. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/definition/update
3. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/definition/on_demand
4. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/definition/delete
5. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/definition/get
6. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/definition/list
7. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/instance/list
8. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/instance/get
9. cluster:admin/opendistro/reports/menu/download
There are already some predefined roles that can be used to manage permissions on reporting:
reports_read_access: permissions 5 to 9.reports_instances_read_access: 7 to 9.reports_full_access: permissions 1 to 9.
More information on how to modify and map roles on the Wazuh Indexer can be found in the Wazuh Indexer documentation.
Upgrade
This section guides you through the upgrade process of the Wazuh indexer.
Preparing the upgrade
In case Wazuh is installed in a multi-node cluster configuration, repeat the following steps for every node.
Ensure you have added the Wazuh repository to every Wazuh indexer node before proceeding to perform the upgrade actions.
Yum
-
Import the GPG key.
rpm --import https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH -
Add the repository.
echo -e '[wazuh]\ngpgcheck=1\ngpgkey=https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH\nenabled=1\nname=EL-$releasever - Wazuh\nbaseurl=https://packages.wazuh.com/5.x/yum/\nprotect=1' | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/wazuh.repo
APT
-
Install the following packages if missing.
apt-get install gnupg apt-transport-https -
Install the GPG key.
curl -s https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH | gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring gnupg-ring:/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg --import && chmod 644 /usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg -
Add the repository.
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/wazuh.gpg] https://packages.wazuh.com/5.x/apt/ stable main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/wazuh.list -
Update the packages information.
apt-get update
Upgrading the Wazuh indexer
The Wazuh indexer cluster remains operational throughout the upgrade. The rolling upgrade process allows nodes to be updated one at a time, ensuring continuous service availability and minimizing disruptions. The steps detailed in the following sections apply to both single-node and multi-node Wazuh indexer clusters.
Preparing the Wazuh indexer cluster for upgrade
Perform the following steps on any of the Wazuh indexer nodes replacing <WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>, <USERNAME>, and <PASSWORD>.
-
Disable shard replication to prevent shard replicas from being created while Wazuh indexer nodes are being taken offline for the upgrade.
curl -X PUT "https://:9200/_cluster/settings" \ -u : -k -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d ' { "persistent": { "cluster.routing.allocation.enable": "primaries" } }'Output
{ "acknowledged" : true, "persistent" : { "cluster" : { "routing" : { "allocation" : { "enable" : "primaries" } } } }, "transient" : {} } -
Perform a flush operation on the cluster to commit transaction log entries to the index.
curl -X POST "https://<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>:9200/_flush" -u <USERNAME>:<PASSWORD> -kOutput
{ "_shards" : { "total" : 19, "successful" : 19, "failed" : 0 } }
Upgrading the Wazuh indexer nodes
-
Stop the Wazuh indexer service.
Systemd
systemctl stop wazuh-indexerSysV init
service wazuh-indexer stop -
Upgrade the Wazuh indexer to the latest version.
Yum
yum upgrade wazuh-indexerAPT
apt-get install wazuh-indexer -
Restart the Wazuh indexer service.
Systemd
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable wazuh-indexer systemctl start wazuh-indexerSysV init
Choose one option according to the operating system used.
a. RPM-based operating system:
chkconfig --add wazuh-indexer service wazuh-indexer startb. Debian-based operating system:
update-rc.d wazuh-indexer defaults 95 10 service wazuh-indexer start
Repeat steps 1 to 3 above on all Wazuh indexer nodes before proceeding to the post-upgrade actions.
Post-upgrade actions
Perform the following steps on any of the Wazuh indexer nodes replacing <WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>, <USERNAME>, and <PASSWORD>.
-
Check that the newly upgraded Wazuh indexer nodes are in the cluster.
curl -k -u <USERNAME>:<PASSWORD> https://<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>:9200/_cat/nodes?v -
Re-enable shard allocation.
# curl -X PUT "https://<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>:9200/_cluster/settings" \ -u <USERNAME>:<PASSWORD> -k -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d ' { "persistent": { "cluster.routing.allocation.enable": "all" } } 'Output
{ "acknowledged" : true, "persistent" : { "cluster" : { "routing" : { "allocation" : { "enable" : "all" } } } }, "transient" : {} } -
Check the status of the Wazuh indexer cluster again to see if the shard allocation has finished.
curl -k -u <USERNAME>:<PASSWORD> https://<WAZUH_INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>:9200/_cat/nodes?vOutput
ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role node.roles cluster_manager name 172.18.0.3 34 86 32 6.67 5.30 2.53 dimr cluster_manager,data,ingest,remote_cluster_client - wazuh2.indexer 172.18.0.4 21 86 32 6.67 5.30 2.53 dimr cluster_manager,data,ingest,remote_cluster_client * wazuh1.indexer 172.18.0.2 16 86 32 6.67 5.30 2.53 dimr cluster_manager,data,ingest,remote_cluster_client - wazuh3.indexer
Uninstall
Note You need root user privileges to run all the commands described below.
Yum
yum remove wazuh-indexer -y
rm -rf /var/lib/wazuh-indexer/
rm -rf /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/
rm -rf /etc/wazuh-indexer/
APT
apt-get remove wazuh-indexer -y
rm -rf /var/lib/wazuh-indexer/
rm -rf /usr/share/wazuh-indexer/
rm -rf /etc/wazuh-indexer/
Backup and restore
In this section you can find instructions on how to create and restore a backup of your Wazuh Indexer key files, preserving file permissions, ownership, and path. Later, you can move this folder contents back to the corresponding location to restore your certificates and configurations. Backing up these files is useful in cases such as moving your Wazuh installation to another system.
Note: This backup only restores the configuration files, not the data. To backup data stored in the indexer, use snapshots.
Creating a backup
To create a backup of the Wazuh indexer, follow these steps. Repeat them on every cluster node you want to back up.
Note: You need root user privileges to run all the commands described below.
Preparing the backup
-
Create the destination folder to store the files. For version control, add the date and time of the backup to the name of the folder.
bkp_folder=~/wazuh_files_backup/$(date +%F_%H:%M) mkdir -p $bkp_folder && echo $bkp_folder -
Save the host information.
cat /etc/*release* > $bkp_folder/host-info.txt echo -e "\n$(hostname): $(hostname -I)" >> $bkp_folder/host-info.txt
Backing up the Wazuh indexer
Back up the Wazuh indexer certificates and configuration
rsync -aREz \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/certs/ \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options.d \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/log4j2.properties \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.keystore \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-observability/ \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-reports-scheduler/ \
/etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-security/ \
/usr/lib/sysctl.d/wazuh-indexer.conf $bkp_folder
Compress the files and transfer them to the new server:
```bash
tar -cvzf wazuh_central_components.tar.gz ~/wazuh_files_backup/
```
Restoring Wazuh indexer from backup
This guide explains how to restore a backup of your configuration files.
Note: This guide is designed specifically for restoration from a backup of the same version.
Note: For a multi-node setup, there should be a backup file for each node within the cluster. You need root user privileges to execute the commands below.
Preparing the data restoration
-
In the new node, move the compressed backup file to the root
/directory:mv wazuh_central_components.tar.gz / cd / -
Decompress the backup files and change the current working directory to the directory based on the date and time of the backup files:
tar -xzvf wazuh_central_components.tar.gz cd ~/wazuh_files_backup/<DATE_TIME>
Restoring Wazuh indexer files
Perform the following steps to restore the Wazuh indexer files on the new server.
-
Stop the Wazuh indexer to prevent any modifications to the Wazuh indexer files during the restoration process:
systemctl stop wazuh-indexer -
Restore the Wazuh indexer configuration files and change the file permissions and ownerships accordingly:
sudo cp etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options /etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options chown wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options sudo cp -r etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options.d/* /etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options.d/ chown wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.options.d sudo cp etc/wazuh-indexer/log4j2.properties /etc/wazuh-indexer/log4j2.properties chown wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/log4j2.properties sudo cp etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.keystore /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.keystore chown wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.keystore sudo cp -r etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-observability/* /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-observability/ chown -R wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-observability/ sudo cp -r etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-reports-scheduler/* /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-reports-scheduler/ chown -R wazuh-indexer:wazuh-indexer /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-reports-scheduler/ sudo cp usr/lib/sysctl.d/wazuh-indexer.conf /usr/lib/sysctl.d/wazuh-indexer.conf -
Start the Wazuh indexer service:
systemctl start wazuh-indexer
Access Control
Wazuh Indexer uses the OpenSearch Security plugin to manage access control and security features. This allows you to define users, roles, and permissions for accessing indices and performing actions within the Wazuh Indexer.
You can find a more detailed overview of the OpenSearch Security plugin in the OpenSearch documentation.
Wazuh default Internal Users
Wazuh defines internal users and roles for the different Wazuh components to handle index management.
These default users and roles definitions are stored in the internal_users.yml, roles.yml, and roles_mapping.yml files on the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch-security/ directory.
Find more info about the configurations files in the Configuration Files section.
Users
| User | Description | Roles |
|---|---|---|
wazuh-server | User for the Wazuh Server with read/write access to stateful indices and write-only access to stateless indices. | stateless-write, stateful-delete, stateful-write, stateful-read, cm_subscription_read |
wazuh-dashboard | User for Wazuh Dashboard with read access to stateful and stateless indices, and management level permissionsfor the monitoring indices. | sample-data-management, metrics-write, metrics-read, stateless-read, stateful-read, cm_update, cm_subscription_write |
Roles
| Role Name | Access Description | Index Patterns | Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|
stateful-read | Grants read-only permissions to stateful indices. | wazuh-states-* | read |
stateful-write | Grants write-only permissions to stateful indices. | wazuh-states-* | index |
stateful-delete | Grants delete permissions to stateful indices. | wazuh-states-* | delete |
stateless-read | Grants read-only permissions to stateless indices. | wazuh-alerts*, wazuh-archives* | read |
stateless-write | Grants write-only permissions to stateless indices. | wazuh-alerts*, wazuh-archives* | index |
metrics-read | Grants read permissions to metrics indices. | wazuh-monitoring*, wazuh-statistics* | read |
metrics-write | Grants write permissions to metrics indices. | wazuh-monitoring*, wazuh-statistics* | index |
sample-data-management | Grants full permissions to sample data indices. | *-sample-* | data_access, manage |
cm_subscription_read | Grants permissions to retrieve subscriptions for the server. | N/A | plugin:content_manager/subscription_get |
cm_subscription_write | Grants permissions to create and delete subscriptions for the content manager. | N/A | plugin:content_manager/subscription_post, plugin:content_manager/subscription_delete |
cm_update | Grants permissions to perform update operations in the content manager. | N/A | plugin:content_manager/update |
Defining Users and Roles
You can create and manage users and roles through the Wazuh Dashboard UI.
Default users and roles cannot be modified. Instead, duplicate them and modify the duplicates.
Creating a New User, Role, and Role Mapping via the Wazuh Dashboard
Prerequisites
- You must be logged in as a user with administrative privileges (e.g.,
admin).
Follow these steps:
1. Create a Role
- In the Wazuh Dashboard, go to Index Management -> Security -> Roles.
- Click Create role.
- Enter a Role name (e.g.,
custom-read-write). - Under Cluster permissions, select permissions if needed.
- Under Index permissions:
- Index: e.g.,
wazuh-* - Index permissions: choose appropriate actions such as:
read(to allow read access)index(to allow write access)
- Optionally, configure Document-level security (DLS) or Field-level security (FLS).
- Index: e.g.,
- Click Create to save the role.
2. Create a User
- In the Wazuh Dashboard, go to Index Management -> Security -> Internal users.
- Click Create internal user.
- Fill in the following:
- Username (e.g.,
new-user) - Password (enter and confirm)
- Description (optional)
- Username (e.g.,
- Click Create to create the user.
3. Verify Role Mapping
When you assign a role to a user during creation, the mapping is created automatically. To review or edit:
- In Security, go to Roles.
- Find and click your role (
custom-read-write). - Go to Mapped users
- Click Map users.
- Fill in the following:
- Users (e.g.,
new-user). - Backend roles (optional).
- Users (e.g.,
- Click Map to save the mapping.
4. Test Access
After creating the user and role:
- Log out from the Dashboard.
- Log in with the new user’s credentials.
- Navigate to Index Management -> Dev Tools.
- Run a query to test access, such as:
GET /wazuh-*/_search